Phosphonic acid
| Structural formula | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

|
|||||||||||||||||||
| General | |||||||||||||||||||
| Surname | Phosphonic acid | ||||||||||||||||||
| other names |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular formula | H 3 PO 3 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Brief description |
white, odorless, crystalline solid |
||||||||||||||||||
| External identifiers / databases | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| properties | |||||||||||||||||||
| Molar mass | 82.00 g mol −1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Physical state |
firmly |
||||||||||||||||||
| density |
1.65 g cm −3 |
||||||||||||||||||
| Melting point |
73 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| boiling point |
259 ° C |
||||||||||||||||||
| pK s value |
|
||||||||||||||||||
| solubility |
very easily soluble in water |
||||||||||||||||||
| safety instructions | |||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||
| Toxicological data | |||||||||||||||||||
| As far as possible and customary, SI units are used. Unless otherwise noted, the data given apply to standard conditions . | |||||||||||||||||||
Phosphonic acid , also outdated phosphorous acid , is a water-soluble, crystalline solid with the empirical formula H 3 PO 3 .
Salts and esters of phosphonic acid are called phosphonates (outdated: phosphites ). The phosphorus in these compounds has the III oxidation state .
Manufacturing
Phosphonic acid is obtained in the laboratory by hydrolysis of phosphorus (III) chloride . The commercial product can be concentrated up to 99.3 percent by heating to 80 ° C.
properties
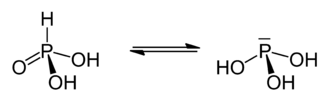
The preferred tautomeric form of phosphonic acid is the structure with doubly bonded oxygen (P = O), which is why it is a two- protonic acid .
The compound disproportionates when heated to form phosphoric acid and highly flammable phosphine .
Organic compounds
Organophosphorus compounds of phosphonic acid with the general structure R – PO (OH) 2 (R = alkyl radical or aryl radical ) and their esters R – PO (OR) 2 (R = alkyl radical) are called phosphonates . The term phosphites , which is outdated for salts , is used for organic compounds with the structure P (OR) 3 ( phosphorous acid ester ). Compounds of this type have important functions in some synthetic processes.
use
Phosphonic acid is used to produce lead phosphonate (a PVC stabilizer), as a reducing agent in chemical processes, as a starting material for the production of phosphonates, such as. B. 1-hydroxyethane-1,1-diphosphonic acid (HEDP, a lime binder used in water softening, in toothpaste, etc.), and used as a long-term retarder in concrete admixtures.
It was discovered by chance in the 1970s that plants treated with phosphonic acid were very well protected against fungi from the Oomycete group . In addition to the preventive effect , a curative (healing) effect could be determined up to a few days after the infection by the fungus. Phosphonic acid is very easily absorbed by the plant and is distributed systemically ( acropetally ) in the plant. The transport takes place in the upper organs (shoot tip, young leaves, flowers, fruit stands) particularly well in the growth phase of a plant. They are also stored in the bills and fruits.
Mode of action
How it works is not yet fully understood, but it is very complex. A direct effect on the fungus is very little. The main reason for the effect is that the fungus gets the phosphonate ion instead of phosphate from tissue enriched with phosphonate . The plant activates its own immune system (= an induced resistance reaction of the plant) so well that infection is prevented and, if an infection has already occurred, the fungal mycelium is killed after a few days and can heal. The substance, which is contained in certain plant strengtheners and foliar fertilizers , is also sometimes used in organic viticulture . In the EU, potassium phosphonates were also approved for organic cultivation until 2013. It is used to combat downy mildew , a disease caused by egg fungi from the order of the Peronosporales. However, it is very disadvantageous that if it is used later (around July) residues can be found in the grapes or in the wine. The risk of residues depends on the time of application and the dose applied. Control measures before and shortly after the vines bloom (beginning to mid-June), cover the most important period of downy mildew control. This prevents residues in the wine (below the detection limit).
Because of the residue problem and because the substance is absorbed into the plant, its use in organic viticulture against downy mildew is still controversial. Phosphonic acid is a very effective substance against downy mildew and is a very good alternative to copper in the pre-bloom area. In extreme conditions, copper is too weak in its effect and even leads to accumulation in humus or soil .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e f g h i Entry on phosphonic acid in the GESTIS substance database of the IFA , accessed on January 28, 2020(JavaScript required) .
- ^ A b A. F. Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 101st edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 1995, ISBN 3-11-012641-9 , p. 769.
- ↑ Entry on Phosphonic acid in the Classification and Labeling Inventory of the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA), accessed on August 1, 2016. Manufacturers or distributors can expand the harmonized classification and labeling .
- ↑ G. Brauer (Ed.), Handbook of Preparative Inorganic Chemistry 2nd ed., Vol. 1, Academic Press 1963, pp. 554-5.
- ↑ K. Drauz, HG Koban, J. Martens, W. Schwarze: Phosphonic and Phosphinic Acid Analogs of Penicillamine , Liebigs Ann. Chem. 1985 , 448-452.
literature
- AF Holleman , E. Wiberg , N. Wiberg : Textbook of Inorganic Chemistry . 101st edition. Walter de Gruyter, Berlin 1995, ISBN 3-11-012641-9 , p. 764.
- Andreas Harm: Use of phosphonates in organic viticulture. In: The winemaker. No. 2/2009, Österreichischer Agrarverlag.