Leaning brick pile
The Leaning Brick Pile (German: slate brick tower ) is an instrument of strategic controlling to the portfolio of a company from the perspective of shareholder value to be analyzed. The market value and book value of the strategic business units of a company are compared.
Action
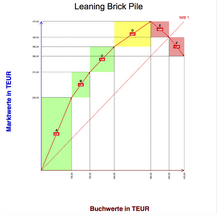
The Leaning Brick Pile is a graphic representation in a two-dimensional coordinate system. The book values (B) of the strategic business units are plotted on the abscissa, their market values (M) on the ordinate. The reason for the tilt of the brick tower lies in the arrangement of the business areas.
First of all, all those business areas are drawn in for which the current market value exceeds the book value, i.e. i.e., whose profitability is greater than the cost of equity. Then the business areas are drawn in, which still have a positive market value, but which no longer reaches the book value. Finally, those business units will be removed that have a negative market value and thus reduce the value of the entire company.
example
A company consists of six strategic business units (SGE A - SGE F). The respective market value and the book value for each SBU were determined. Then the ratio of market value to book value was established and the business units were then arranged in descending order.
| Strategic business unit |
Market value | Book value | M / B ratio | Rank according to M / B ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBU A | € 230 million | € 100 million | 2.33 | 1 |
| SBU B | € 80 million | € 60 million | 1.33 | 2 |
| SBU C | € 80 million | € 80 million | 1.00 | 3 |
| SGE D | € 80 million | € 120 million | 0.67 | 4th |
| SGE E | −50 million € | € 60 million | −0.83 | 5 |
| SGE F | −60 million € | € 50 million | −1.2 | 6th |
For SGE A and SGE B, the ratio of market value to book value is greater than 1, i.e. In other words, they contribute to increasing the company's value. With SGE C the market value corresponds to the book value of the invested capital, i. H. the business unit can at least earn interest on the capital employed. SGE D contributes to the company's value with a positive market value. However, this is below the book value. SGE E and SGE F reduce the company value due to their negative market value.
advantages
Leaning Brick Pile gives an overview of the value contribution of each strategic business unit and can be helpful in this regard to check the dimensions of the company. It also allows conclusions to be drawn from strategic decisions in the respective business units on the overall situation of the company.
disadvantage
The Leaning Brick Pile clearly shows the value contribution of each business unit, but cannot capture the key value drivers. Synergies between the business units are not recorded.
literature
- Baum, Heinz Georg; Coenenberg, Adolf G .; Günther, Thomas: Strategic Controlling . Schäffer-Poeschel publishing house. Stuttgart 2007, ISBN 978-3-7910-2545-2
- Günther, Thomas: Corporate value-oriented controlling . Publisher Franz Vahlen. Munich 1997, ISBN 3-7910-2114-1
- Hax, Arnoldo C .; Majluf, Nicolas S .: Strategic Management. An integrative concept from MIT . Campus publishing house. Frankfurt (a. M.) / New York 1991, ISBN 3-593-34554-4
- Höfner, Klaus; Pohl, Andreas (ed.): Value increase management. The shareholder value concept: methods and successful examples . Campus publishing house. Frankfurt (a. M.) / New York 1994, ISBN 3-593-35122-6