Melanosis coli
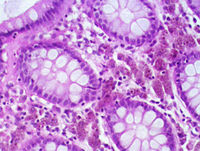
As melanosis coli (synonym: pseudomelanosis coli) (gr. Melanos "black"; lat. Colon "colon") is an innocuous, patchy darkening of the large intestine called mucosa. It is based on increased pigmentation of the lamina propria due to activation of macrophages , which phagocytize the pigment lipofuscin . This finding has only been documented since colonoscopy was widely used . There is no evidence of association with pathological processes.
The most common cause is seen to be the constant use of laxatives . Melanosis coli must not be confused with Peutz-Jeghers syndrome , which can also lead to hyperpigmentation of the gastrointestinal tract .
Preparation of the colon mucosa in melanosis coli (numerous pigment-laden macrophages can be seen )
Web links
Commons : Melanosis coli - Collection of pictures, videos and audio files