Hacksaw
A hacksaw is a saw that is used to cut metal workpieces in two or, in some cases, to shape them. For this purpose, the machine saw is designed with regard to feed and cutting speed and stability and is equipped with special auxiliary devices such as cooling lubricant supply that are only required for metalworking . Metal hand saws, on the other hand, are conventional saws, but the saw blade is adapted to the material.
Components
A hacksaw consists of:
- the saw blade or an endless saw band. This element carries out the actual processing of the material.
- a holder or guide device that holds and guides the sheet or tape, e.g. B. a bracket or guide rollers and rails
- a power transmission device, e.g. B. a handle or a motor
- possibly a workpiece holder
Mark
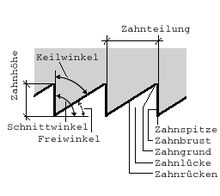
Hacksaws cut relatively tough materials. The saw blades therefore have compared to z. B. wood saws have a finer pitch (more teeth per unit length). The saw blades are made of hard and tough material. Due to the height of the saw blade, the cuts can only be made straight or with a limited radius.
Working method
The saw blade is driven uniformly or in an oscillating manner and pressed onto the workpiece. Due to the shape of each individual tooth, a chip of the basic material is removed and transported out of the cut with each cutting stroke. There are always several cutting edges of the saw blade in contact with the workpiece. For a successful sawing, parameters such as saw blade and pitch, cutting speed, infeed and, if necessary, cooling lubricant are decisive. The shape of the cutting edges in turn depends on the material of the workpiece. So is z. For example, the softer the material, the smaller the cutting angle (comparison aluminum-steel).
variants
Metal saws are available as
- Hacksaws , hand or machine driven
- Band saws
- Circular saws