Morgan Walls reaction
The Morgan-Walls reaction is a name reaction used in organic chemistry for the synthesis of phenanthridine and phenathridine derivatives . It goes back to the British chemists Gilbert Thomas Morgan (1872-1940) and Leslie Percy Walls . They developed the synthesis in 1931 to optimize the Pictet-Hubert reaction . The Morgan-Walls reaction describes the intramolecular ring closure of an N - acyl - 2-aminobiphenyl in the presence of phosphorus oxychloride .
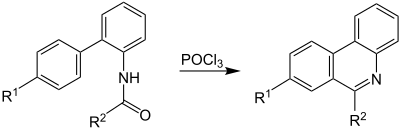
Overview reaction
The following equation gives an overview of the Morgan-Walls reaction. An N- acyl-2-aminobiphenyl reacts with phosphorus oxychloride to form a phenantridine derivative with ring closure. R 1 and R 2 are organic radicals :
The Morgan-Walls reaction can be used in particular for the synthesis of phenanthridine:
Reaction mechanism
In the following, a possible reaction mechanism for the Morgan-Walls reaction will be explained based on the synthesis of phenanthridine according to the second overview reaction equation:
First, the starting compound 1 is attacked on the formyl group by the phosphorus oxychloride, with HCl being split off. Then the ring closes with elimination of phosphorodichloridate, so that intermediate stage 2 is formed. At this intermediate stage, the hydrogen atom in bold is explicitly drawn in to illustrate the next reaction step. This hydrogen atom is finally split off as a proton, so that intermediate stage 2 is deprotonated and the end product phenanthridine is formed.
Pictet-Hubert reaction
The Pictet-Hubert reaction is another name reaction in organic chemistry from which the Morgan-Walls reaction emerged. It was discovered in 1896 by the Swiss chemists Amé Pictet (1857–1937) and A. Hubert. This reaction is also used for the synthesis of phenanthridine derivatives and essentially differs from the Morgan-Walls reaction in that it uses zinc chloride instead of phosphorus oxychloride.
Individual evidence
- ^ Gilbert Thomas Morgan, Leslie Percy Walls: CCCXXXV. — Researches in the phenanthridine series. Part I. A new synthesis of phenanthridine homologues and derivatives . In: Journal of the Chemical Society . 1931, p. 2447-2456 , doi : 10.1039 / JR9310002447 .
- ↑ Jie Jack Li: Name reactions: A collection of detailed mechanisms and synthetic applications . 5th ed. Cham 2014, ISBN 978-3-319-03979-4 , pp. 413-414 , doi : 10.1007 / 978-3-319-03979-4 .
- ^ Daniel D. Holsworth: Name reactions in heterocyclic chemistry . Ed .: Jie Jack Li. Wiley, Hoboken, NJ 2005, ISBN 978-0-471-70415-7 , pp. 465-468 , doi : 10.1002 / 0471704156.ch9 .
- ↑ Amé Pictet, A. Hubert: About a new synthesis of phenanthridine bases . In: Reports of the German Chemical Society . tape 29 , no. 2 , 1896, p. 1182-1189 , doi : 10.1002 / cber.18960290206 .