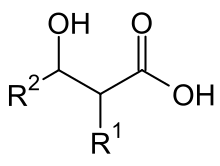
Mycolic acids
Mycolic acids are long-chain, branched fatty acids that occur in the cell walls of mycobacteria , rhodococci , nocardia and corynebacteria . They are part of the acid-resistant cell wall . The storage of mycolic acids makes the cells highly hydrophobic .
Mycolic acids are the longest naturally occurring fatty acids. They are bound to the Murein via arabinogalactan .
literature
- K. Takayama, C. Wang, GS Besra: Pathway to synthesis and processing of mycolic acids in Mycobacterium tuberculosis. In: Clin Microbiol Rev. 2005 Jan; 18 (1), pp. 81-101. PMID 15653820 . PMC 544180 (free full text)
- EK Schroeder, N. de Souza, DS Santos, JS Blanchard, LA Basso: Drugs that inhibit mycolic acid biosynthesis in Mycobacterium tuberculosis . In: Curr Pharm Biotechnol . tape 3 , no. 3 , September 2002, p. 197-225 , PMID 12164478 .
- M. Watanabe, Y. Aoyagi et al .: Separation and characterization of individual mycolic acids in representative mycobacteria. In: Microbiology. Volume 147, Pt 7 July 2001, pp. 1825-1837. PMID 11429460 .