Odontoplasty
Under odontoplasty ( Greek: ὀδών ὀδούς -odon, odonto- "tooth", πλάττειν, pláttein - form, form, shape; English: Tooth shaping) is understood in dentistry as the reshaping of teeth for aesthetic reasons, in the context of an orthodontic Therapy or to improve hygiene in the case of misaligned teeth. To do this, teeth are ground down slightly in the enamel area .
Odontoplasty consists of subtractive measures in the enamel area of one or more teeth . Odontoplasty should be differentiated from changes in the tooth shape through additive measures, such as build-ups using composites (plastics), veneers (veneers) or chips (partial veneers). In some cases, both procedures are combined in one overall treatment. A special form of odontoplasty is furcation plastic as part of periodontal therapy.
Preventive odontoplasty
For caries prophylaxis, teeth can be narrowed in the lower jaw front, for example in the case of crowded front teeth, in order to reduce plaque retention sites . Likewise, niches, furrows or recesses that are difficult to reach with a toothbrush can be remodeled and smoothed.
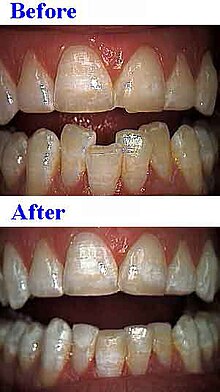
Aesthetic odontoplasty
Elongated (lengthened) teeth can be shortened so that the cutting edge runs in one line. If an upper lateral incisor is not positioned more frequently, the canine can be orthodontically moved to fill the gap in place of the lateral incisor. The canine can then be reground in the shape of a lateral incisor. A slightly rotated tooth can be optically "rotated" by combining the removal of tooth substance on one side and the application of composite.
Orthodontic odontoplasty
If there is a disproportion between the size of the arch and the width of the front teeth, space can be gained by reducing the enamel in the approximal areas (interdental spaces) in order to carry out minor corrections to the position of the teeth as part of an orthodontic treatment.
Furcation plastic
Plaque retention points in furcations (root bifurcations) of the lower molars in the case of grade III furcations and widely divergent roots can be removed by light grinding.
Reward
Neither the private fee schedule for dentists (GOZ) nor the assessment standard for dental services (BEMA) for statutory health insurance patients provide for a fee item for an odontoplasty. The service must therefore be calculated in accordance with Section 6 (1) of the GOZ, according to which independent dental services that are not included in the list of fees can be calculated according to a service of the list of fees that is equivalent in terms of type, cost and time expenditure .
Individual evidence
- ↑ Markus Firla: Tooth shaping: subtractive aesthetic tooth shape corrections . Spitta Verlag GmbH & Co. KG, 2005, ISBN 978-3-938509-02-9 , p. 17 ( google.com ).
- ↑ EM Rateitschak, KH Rateitschak: Parodontologie . Georg Thieme, 2004, ISBN 978-3-13-655603-0 , p. 388 ( google.com ).
- ↑ E. Hellwig, J. Klimek, Thomas Attin: Introduction to tooth preservation . Deutscher Ärzte-Verlag GmbH, 2013, ISBN 978-3-7691-3448-3 , p. 572 ( google.com ).
- ↑ Schedule of Fees for Dentists (GOZ) 2012 (PDF; 3.0 MB)