Overhauled
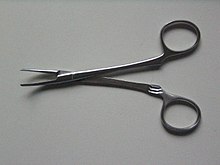
The so-called Overholt is a slightly curved Dissecting with cusped, but rounded ends of the branches without dentition, not always with a lock (in the image as a raster hereinafter) provided an irreplaceable surgical instrument, which in various sizes and even in the endoscopy represented is. It belongs to the group of instruments to be grasped .
The Overholt was named after the thoracic surgeon and lung specialist Richard Overholt , born in 1901, founder of the Overholt Thoracic Clinic in Boston, Massachusetts.
construction
Overhauled are usually made of stainless steel. This makes them easy to sterilize.
The handle is designed with glasses because the overholt has no spring and must be sheared sideways to open. It sometimes has a two-stage notch, but there are also examples without a lock (clasp). The branches are long but powerful. Since the Overholt is usually not used for sewing, it has a simple but strong hinge.

The jaws are grooved to prevent slipping off the specimen. They are usually bent slightly sideways. This happens for three reasons:
- you can stop by the Overholt and see WHAT you have grasped there
- you can put the overholt so well on the edge of the operating theater and have a good view
- it can be held in such a way when tying a ligature that the knot can be pushed down safely with a finger.
Overholt clamps are usually not coated with hard metal.
use
The Overholt is the standard dissecting clamp:
- Loose tissue is butt separated by spreading it,
- Vessels can be undercut and freed from adventitia,
- Threads (for ligature purposes), rubber reins or small catheters can be pulled through.
- Small arteries that bleed into the surgical area can be clamped with the same instrument and, due to their curved shape, easily attached to the vessel stump with a ligature .
But this can also be done with another short, curved clamp with a lock (short vascular clamp), the so-called mosquito , which, unlike the Overholt, is unsuitable for dissection because of its shortness.