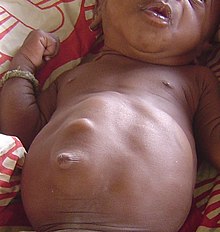
Diastasis recti
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| M62.08 | Muscle diastasis: other |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
The straight abdominal muscles ( Mm. Recti abdominis ) in the area of the linea alba are described as recti diastasis ( old Gr . Διἀστασις diástasis "space", "distance") . It can be observed or acquired as a congenital abnormality . In Germany, a diastasis rectus over two centimeters is currently considered a pathological finding.
Expression and cause
A diastasis recti is usually between 2 and 10 cm wide and between 12 and 15 cm long; in extreme cases, however, a width of up to 30 cm has also been observed. The gap is usually most pronounced in the area of the navel . Since the rectus sheath consists only of the anterior leaf from the arcuate line , diastasis rectus occurs more frequently above the navel.
Women are particularly affected; diastasis recti is often a result of pregnancy and childbirth, especially after multiple births. Possible causes for the acquired form are, for example, overweight ( obesity ) or heavy straining such as during childbirth or chronic constipation (constipation). Other risk factors include: the pregnant woman's age over 35, multiple pregnancies , a high birth weight of the newborn, and excessive abdominal exercise after the end of the first trimester of pregnancy.
Physiological diastasis recti is also caused by normal pregnancy from around the fifth month of pregnancy. After that, the crevice can gradually recede - usually within a few months after the birth. During this time, strenuous physical activity, especially lifting heavy loads, should be avoided. Women are advised to under instruction in childbirth and in the subsequent period to the prevention exercises Rückbildungsgymnastik conduct in which first the cross and also the obliques and the long abdominal muscles are strengthened later.
Symptoms
The muscles of the abdominal wall become increasingly inadequate when the diastasis rectus increases, because on the one hand the lever arm of the Mm. recti abdominis becomes more and more unfavorable with greater divergence and on the other hand the oblique lateral abdominal muscles lose their necessary tension. Due to the insufficiency of the abdominal wall, the abdominal pressure deteriorates because the necessary intra-abdominal pressure can no longer be built up.
The diastasis recti also predisposes to abdominal wall ruptures. The incidence of incisional hernias is particularly increased after surgical interventions in the abdomen.
diagnosis
The diastasis recti can be palpated while lying down when the patient is lying on their back and lifts their head. When the upper body is lifted, the intestines also turn forward. A deepening of the umbilical region can also tend to be recognizable when standing. In slim people, a diastasis rectus becomes visible when the abdomen is pressed as a bulging of the abdomen in this area.
The diastasis recti must be distinguished from an abdominal wall hernia . In addition to clinical examinations, sonography, CT and MRI can be used for diagnosis.
treatment
The symptoms of a diastasis rectus can possibly be relieved through physiotherapy exercises ("Exercises according to Angela Heller").
An operation indication (to “gather up the rectus sheath ”) exists in the case of persistent complaints caused by the relaxation of the insufficient abdominal muscles.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b abdominal muscles. Retrieved July 10, 2013 .
- ^ A b Angela Heller: After the birth: puerperium and regression . Georg Thieme Verlag, 2002, ISBN 978-3-13-125041-4 , p. 136
- ↑ a b Edvin Turkof, Elis Sonnleitner: Chapter " Diastasis rectus" ,. (PDF; 416 kB) (No longer available online.) Archived from the original on June 26, 2013 ; Retrieved July 10, 2013 (Volume 8, Pages 30-32). Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Why do abdominal muscles sometimes separate during pregnancy? Mayo Clinic, October 30, 2014 (in English).
- ↑ Diastasis recti after pregnancy. Retrieved July 10, 2013 .