Rocker bogie
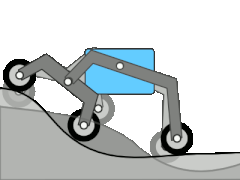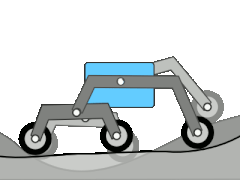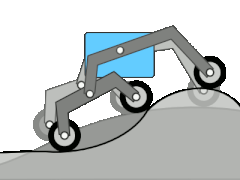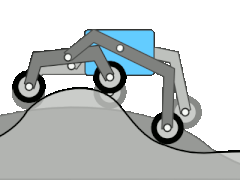
The rocker bogie system is a landing gear that has been used on various Mars rovers . Rocker means something like seesaw and relates to the suspension of the wheels. This can compensate for unevenness in the floor. The two large rockers are connected to the chassis via a differential . This means that the chassis moves relatively little even with large movements of the individual wheels or seesaws. Since all six wheels are individually driven by independent motors, obstacles that are larger than one wheel diameter can also be overcome. On the Mars Exploration Rovers and Curiosity , the front and rear wheels can each be rotated individually around a vertical axis. In addition to the usual steering tasks, i.e. driving around bends, turning on the spot can also be carried out in a simpler way than with a crawler chassis.
Previous rovers with the rocker bogie system
- In 1996 the little rover Sojourner landed on Mars with the Mars probe Mars Pathfinder , with which the rover technology, including the rocker-bogie landing gear, was thoroughly tested.
- In 2003, the rovers Spirit and Opportunity of the Mars Exploration Rover program landed on Mars. Both rovers exceeded the planned minimum deployment time many times over. Opportunity had been in action for fourteen years until the mission ended in February 2019 (after losing radio contact in the summer of 2018). There has been no contact with Spirit since 2010.
- In 2012 the largest rover to date landed on Mars: The Mars Science Laboratory (also known as Curiosity ).
Web links
- Video for rocker-bogie (Engl.)