Stone format
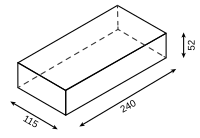
The formats of artificial bricks ( concrete block according to DIN 18151/18152, sand-lime brick according to DIN 106, aerated concrete according to DIN 4165 and bricks according to DIN 105) are usually named with abbreviations (e.g. 2 DF). In construction it is common to use format abbreviations that refer to a multiple of the so-called thin format (240 × 115 × 52 mm).
The dimensions of various formats are regulated in the respective product standards. These are based on the standard building dimensions of the octametric (1/8 m = 12.5 cm) grid of DIN 4172. The layer size (whole number of the octameter grid) results from the stone height and the bed joint height.
The stone height depends on the mortar height (normal mortar approx. 1.2 cm, thin-bed mortar 1 to 3 mm).
In addition to the thin format (DF), the normal format (NF) is still used today in the area of facing masonry. In contrast to stones based on the thin format (240 × 115 × 52 mm), with stones from the normal format (240 × 115 × 71 mm) the octametric grid is only achieved after three layers. Historical formats such as B. the Reichsformat (250 × 120 × 63 mm) are no longer produced in series.
Layer dimensions depending on the stone height
|
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Formats and names
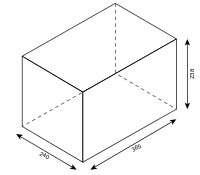
The abbreviations are clear up to format 3 DF and can therefore be used when ordering. From format 4 DF this uniqueness is no longer given and additional information (the wall thickness) is required. This is especially the case when stones with a tongue and groove system are used, which therefore cannot be rotated at will. For example, a 4 DF can have the following dimensions:
| designation | Length × width × height |
|---|---|
| 4 DF (115) for normal mortar | (248 × 115 × 238) |
| 4 DF (115) for thin bed mortar | (248 × 115 × 248) |
| 4 DF (240) for normal mortar | (248 × 240 × 113) |
| 4 DF (240) for thin bed mortar | (248 × 240 × 123) |
The following table shows examples of brick formats offered by German manufacturers:
| designation | Dimension / wall thickness | |
|---|---|---|
| DF (thin format) | (240 × 115 × 52) | |
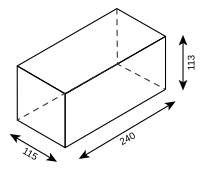
| NF (normal format) | (240 × 115 × 71) | |
| (115 × 240 × 71) | ||
| 2 DF | (240 × 115 × 113) | |
| 2 DF | (115 × 240 × 113) | |
| 3 DF | (240 × 175 × 113) | |
| 3 DF | (175 × 240 × 113) | |
| 5 DF (240) | (300 × 240 × 113) | |
| 5 DF (300) | (240 × 300 × 113) | |
| 6 DF (240) | (365 × 240 × 113) | |
| 6 DF (365) | (240 × 365 × 113) | |
| 10 DF (240) | (300 × 240 × 238) | |
| 10 DF (300) | (240 × 300 × 238) | |
| 12 DF (240) | (365 × 240 × 238) | |
| 12 DF (365) | (240 × 365 × 238) | |
| 20 DF | (498 × 300 × 238) | |
| 24 DF | (498 × 365 × 238) |
swell
- Klaus-Jürgen Schneider (founder), Alfons Goris, Klaus Berner: Construction tables for engineers. 17th edition. Werner, Neuwied 2002, ISBN 978-3-8041-5228-1
- Hans Rich: Sand-lime brick, the mason's primer. 7th edition. Construction and Technology, Düsseldorf 2004, ISBN 978-3-7640-0453-8 .