Cessna T-37
| Cessna T-37 tweet | |
|---|---|

|
|
| Type: | Jet trainer |
| Design country: | |
| Manufacturer: | |
| First flight: |
October 12, 1954 |
| Commissioning: |
1957 |
| Production time: |
1955 to 1975 |
| Number of pieces: |
1,272 |
The Cessna T-37 Tweet is a subsonic twin- engine trainer aircraft used by many air forces. Until 2009 this also included the German Air Force . The two seats of the machine are arranged next to each other, which enables the flight instructor to “watch the student's hands” and to address any errors directly.
history
The Tweet was developed in the early 1950s and in December 1952 won the United States Air Force (USAF) tender for a new trainer aircraft as the Cessna Model 318 . At this, no fewer than eight companies presented a total of fifteen designs. Three XT-37 prototypes were ordered from Cessna, the first of which made its maiden flight on October 12, 1954 in Wichita with test pilot Bob Hagan on board. After eleven pre-series T-37 aircraft, the first of 524 series T-37A aircraft built was completed in mid-1955, which took off on its maiden flight on September 27. In September 1956, the aircraft was officially entered into service as a replacement for the T-34 Mentor in the USAF, and cadet training on it began in 1957.
The USAF ordered 444 T-37s that were delivered through 1959. In 1957, the Air Force tried to convert the T-37 for combat tasks, but then decided on the Grumman OV-1 Mohawk .
The USAF was happy with the T-37A, but it was underpowered. That is why the T-37B was developed, which with the new Continental J69-T-25 had 10% more thrust. In addition, the avionics have been revised.
From 1959 to 1973 552 T-37Bs were built and the existing T-37A were upgraded to such (466 newly built, the rest converted).
Neither the T-37A nor the T-37B had weapon systems or external weapon pylons. In 1961, Cessna began developing the T-37C, an export version with a 650 kg higher take-off mass that was designed for light attack tasks. Of this machine, equipped with a sight and two external load stations for 155 kg each (e.g. containers for 12.7 mm MG or rockets), a total of 269 pieces were built.
Based on the cells of the T-37B / C, the two prototypes YAT-37D of the A-37 , which had its first flight on October 23, 1963 and is a light combat version of the aircraft, were also created.
In 1986 a complete overhaul of the T-37 (called T-48) with a modern cockpit and new engines (Garret-F109) was proposed, but this was not pursued. After more than 50 years, the last seven T-37B machines were officially decommissioned on July 31, 2009 at Sheppard Air Force Base in Texas.
A total of 1,272 machines of the various versions of the T-37 (including prototypes) were built.
production
The aircraft was also delivered to friendly nations as part of the Military Aid Program (MAP).
Acceptance of the T-37 by the USAF:
| version | 1954 | 1955 | 1956 | 1957 | 1958 | 1959 | 1960 | 1961 | 1962 | 1963 | 1964 | 1965 | 1966 | 1967 | 1968 | 1969 | 1970 | 1971 | 1972 | 1973 | 1974 | 1975 | 1976 | 1977 | TOTAL |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| XT-37 | 2 | 1 | 2 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Static test | 1 | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| T-37A | 2 | 15th | 90 | 156 | 150 | 413 | |||||||||||||||||||
| T-37B | 30th | 146 | 82 | 7th | 14th | 44 | 84 | 77 | 5 | 489 | |||||||||||||||
| T-37C | 4th | 4th | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| T-37C MASF | 6th | 6th | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| T-37B MAP | 40 | 24 | 5 | 69 | |||||||||||||||||||||
| T-37B Germany | 14th | 33 | 47 | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| T-37C MAP | 4th | 24 | 34 | 30th | 2 | 3 | 11 | 11 | 119 | ||||||||||||||||
| T-37C Peru | 6th | 6th | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| T-37C Chile | 4th | 4th | |||||||||||||||||||||||
| T-37C Pakistan | 5 | 1 | 5 | 7th | 18th | ||||||||||||||||||||
| TOTAL | 2 | 3 | 16 | 90 | 156 | 180 | 146 | 82 | 51 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 48 | 44 | 89 | 78 | 16 | 2 | 3 | 11 | 0 | 11 | 0 | 7th | 1,175 |
rating
Both trainers and students describe the T-37 as a good and robust training aircraft. It is easy to fly and most classic flight maneuvers can be practiced with it. The side-by-side (ejector) seats allow the flight instructor a good view of his student and the two engines offer additional security against failure. Its only disadvantage is its enormous volume, even for a jet aircraft from the 1950s, due to the loud, high-frequency sound of the engines, which earned it the nickname " Tweety Bird ".
Armament
The T-37A and T-37B were pure jet trainers and therefore unarmed.
The export version of T-37C had room each on two pylons for General Electric - automatic cannon mm with 200 rounds of caliber 12.7, two 70-mm rockets or up to four (exercise) bombs.
User states
-
 Bangladesh : 30
Bangladesh : 30 -
 Brazil : 65 T-37C (later 30 of them came to South Korea and 12 to Paraguay )
Brazil : 65 T-37C (later 30 of them came to South Korea and 12 to Paraguay ) -
 Chile : 20 T-37B and 12 T-37C
Chile : 20 T-37B and 12 T-37C -
 Ecuador : 10 T-37B
Ecuador : 10 T-37B -
 Germany : 47 T-37B purchased; all decommissioned
Germany : 47 T-37B purchased; all decommissioned -
 Greece : 8 T-37B and 24 T-37C
Greece : 8 T-37B and 24 T-37C -
 Cambodia : 4 T-37B
Cambodia : 4 T-37B -
 Colombia : 4 T-37B and 10 T-37C
Colombia : 4 T-37B and 10 T-37C -
 Jordan : 15 former US T-37Bs
Jordan : 15 former US T-37Bs -
 Morocco : 14
Morocco : 14 -
 Myanmar : 12 T-37C
Myanmar : 12 T-37C -
 Pakistan : 24 T-37B and 39 T-37C
Pakistan : 24 T-37B and 39 T-37C -
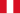 Peru : 32 T-37B
Peru : 32 T-37B -
 Portugal : 30 T-37C
Portugal : 30 T-37C -
 South Korea : 25 T-37C and later 30 T-37C from Brazil
South Korea : 25 T-37C and later 30 T-37C from Brazil -
 South Vietnam : 24 T-37B
South Vietnam : 24 T-37B -
 Thailand : 10 T-37B and 6 T-37C
Thailand : 10 T-37B and 6 T-37C -
 Turkey : 50 T-37C
Turkey : 50 T-37C -
 United States
United States
-
 Vietnam : captured T-37 of the former South Vietnamese Air Force
Vietnam : captured T-37 of the former South Vietnamese Air Force
Use for the German Air Force
The T-37B, officially owned by the German Armed Forces, flew with USAF license plates as they were stationed at Sheppard Air Force Base ( Texas ) in the USA . There, since the T-37 on the Beechcraft T-6 was retired, the German flight students receive their flying training within 55 calendar weeks as part of the Euro NATO Joint Jet Pilot Training, or ENJJPT for short. The responsibility for the training lies in the hands of the 80th Flying Training Wing of the USAF.
Use in Portugal
The Portuguese specimens also belonged to the Asas de Portugal ( Wings of Portugal ), the Portuguese aerobatic team, since 1977 .
future
After more than 40 years in service, the T-37s are now slowly being phased out. They will be replaced by the Beechcraft T-6A Texan II , a turboprop aircraft with modern avionics.
Technical specifications
| Data | T-37A | T-37B | T-37C |
|---|---|---|---|
| task | Subsonic trainer aircraft | ||
| Manufacturer | Cessna | ||
| crew | Instructors and students | ||
| length | 8.92 m | ||
| height | 2.80 m | ||
| span | 10.26 m | ||
| Gauge | 4.28 m | ||
| wheelbase | 2.36 m | ||
| Wing area | 17.09 m² | ||
| Empty mass | 1,755 kg | ||
| Max. Takeoff mass | 2,903 kg | 2,995 kg | 3,630 kg |
| Top speed in 7620 m | ? km / h | 684 km / h | 647 km / h |
| Cruising speed in 7620 m | ? km / h | 612 km / h | 574 km / h |
| Stall speed | ? km / h | 134 km / h | 143 km / h |
| Service ceiling | ? m | 10,700 m | 9,115 m |
| Rate of climb | ? m / s | 17.3 m / s | 10.7 m / s |
| Take-off distance over a 15 m obstacle | ? m | 760 m | 840 m |
| Landing distance over a 15 m obstacle | ? m | 775 m | 1,035 m |
| Range | ? km | 1,065 km | 1,515 km with wing end tanks |
| Engine | 2 × YJ69-T-9 with 4.1 kN each | 2 × J69-T-25 with 4.56 kN each | |
See also
Web links
- Air Force: Cessna T-37
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b FlugRevue October 2008, pp. 59–62, aircraft down to the smallest detail - Cessna T-37
- ↑ Statistical Digest of the USAF 1954, pp. 70 f .; 1955, p. 80 f .; 1956, p. 91 f .; 1957, p. 97 f .; 1958, p. 72 f .; 1959, p. 68 f .; 1960, p. 62 f .; 1961, p. 70 f .; 1962, p. 72 f .; 1963, p. 71 f .; 1964, p. 58 f .; 1965, pp. 60 f .; 1966, p. 115 f .; 1967, p. 122 f .; 1968, p. 132 f .; 1969, p. 111 f .; 1970, p. 107 f .; 1971, p. 102 f .; 1972, p. 154 f .; 1973, p. 52 f .; 1974, p. 48 f .; 1975, p. 52 f .; 1976, p. 80 f .; 1977, p. 55 f.