Gilan
| Gilan | |
|---|---|
| Location of Gilan Province in Iran | |
| Basic data | |
| Country | Iran |
| Capital | Rascht |
| surface | 14,042 km² |
| Residents | 2,530,696 (2016 census) |
| density | 180 inhabitants per km² |
| ISO 3166-2 | IR-19 |
Coordinates: 37 ° 19 ' N , 49 ° 31' E


Gilan ( Persian گيلان, DMG Gīlān ) is one of 31 provinces of Iran . The capital is Rasht .
2,530,696 people live in the province (2016 census). The province on the Caspian Sea covers 14,042 square kilometers and has a population density of 180 inhabitants per square kilometer.
geography
Gilan is characterized by a humid climate, lies in the north of Iran and borders the Caspian Sea in the north, the Ardabil province in the west, the Mazandaran province in the east and the Zanjan and Qazvin provinces in the south .
Gilan contains the cities of Astara , Astaneh Ashrafiyeh , Bandar Anzali , Rascht, Rudbar , Rudsar , Somiyehsara , Fuman , Lāhidschān , Langerud , Talesch and Shaft according to the last administrative division in 1996 .
population
In 1996, 46.8% of the population lived in cities and 53.2% in rural areas. Most residents speak Gilaki as their first language . In addition, Taleschi is spoken in the northwest of the province ( Talesch ) . For several decades, however, dominated in some areas Taleschs Azeri , with the Turkish language related to the Azerbaijani population from the north-west Iran (the provinces of Ardebil , and West and East Azerbaijan ). Smaller minorities speak Galeschi, Kurdish , Tati and Domari ( Roma ).
history
The Iron Age burial ground of Amlasch is in the province of Gilan.
In the course of the Russo-Persian War (1722–1723) , Russian troops occupied the city of Rasht in late autumn 1722 , supposedly to protect it. In February 1723 the governor of the city assured that the Persian troops could ensure security themselves and that the Russians would please leave. The Russians, however, broke their promise to withdraw their troops; they were therefore besieged in their barracks. At the end of March 1723, the Russian troops broke out, killing more than 1000 Persian soldiers and forcing the Persian Shah Tahmasp II to negotiate. His ambassador, Ismail Beg, had to sign the humiliating Treaty of Saint Petersburg in September 1723 . One of the provisions of this treaty was that Gilan would be ceded to Russia.
The Russian Emperor Peter the Great wanted to annex the newly acquired territories permanently to Russia. He had the castles Derbent and Heiligkreuz expanded and information about the economic basis of the conquered regions sent to him. In May 1724 he wrote to the Russian commander of Rasht to invite Armenians and other Christians to Gilan and Mazandaran and settle them, while the number of Muslims should be quietly reduced so that they would not notice. In practice, however, the Russian occupation caused great economic damage. Silk production fell sharply and did not recover for many years because the silk makers had fled the province. For Russia the occupation of the Persian provinces was expensive; more than half of the soldiers did not return from the campaign. The successors of Peter the Great decided to make peace with Persia, even if the occupied provinces would have to be returned. The Rasht Treaty of 1732 stipulated that Gilan would be returned to Persia.
Thereafter, Gilan and its capital Rasht were occupied by Russia and the Soviet Union respectively in 1909 / 11-12, 1915-18 (Gilan as a Russian puppet republic), 1920-21 and 1941-46 . The Iranian Soviet Republic was established here.
Administrative division
The province of Gilan is divided into twelve counties:
| map | abbreviation | district |
|---|---|---|
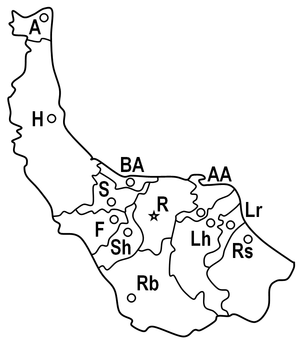
|
||
| A. | Astara | |
| AA | Astaneh-e Ashrafiyyeh | |
| BA | Bandar Anzali | |
| F. | Fuman | |
| H | Haschtpar | |
| Lh | Lahijan | |
| Lr | Langarud | |
| R. | Rascht | |
| Rs | Rudsar | |
| Rb | Rudbar | |
| S. | Some'e Sara | |
| Sh | Shaft |
Colleges
- University of Gilan
- Islamic Azad University of Astara
- Islamic Azad University of Bandar Anzali
- Islamic Azad University of Rasht
- Islamic Azad University of Lahijan
- Islamic Azad University of Talesh
- Gilan University of Medical Sciences
- Institute of Higher Education for Academic Jihad of Rasht
- Technical & Vocational Training Organization of Gilan
See also
- Administrative divisions of Iran
- Iranian Soviet Republic
- Caspian Hyrcania mixed forest
- Ganj Par , old Paleolithic site on Sefid Rud
- Marlik , archaeological site
literature
- Yukako Goto: The southern Caspian provinces of Iran under the Safavids in the 16th and 17th centuries . Berlin, Klaus Schwarz Verlag 2011. ISBN 978-3-87997-382-8
Web links
- Gilan entry in the Encyclopædia Iranica
- Guilan University of Medical Sciences Health Information Center
- Gilan Cultural Heritage Organization (An excellent source of info in Persian)
- Guilan Province Office of Tourism
Individual evidence
- ↑ City Population: Iran - Cities and Provinces .
- ↑ Firuz Kazemzadeh: Iranian relations with Russia and the Soviet Union, to 1921 . In: Peter Avery, Gavin Hambly and Charles Melville (Eds.): The Cambridge History of Iran . tape 7 . Cambridge University Press, 1991, ISBN 978-0-521-20095-0 , pp. 318 .
- ↑ a b Firuz Kazemzadeh: Iranian relations with Russia and the Soviet Union, to 1921 . In: Peter Avery, Gavin Hambly and Charles Melville (Eds.): The Cambridge History of Iran . tape 7 . Cambridge University Press, 1991, ISBN 978-0-521-20095-0 , pp. 321 .
- ↑ Firuz Kazemzadeh: Iranian relations with Russia and the Soviet Union, to 1921 . In: Peter Avery, Gavin Hambly and Charles Melville (Eds.): The Cambridge History of Iran . tape 7 . Cambridge University Press, 1991, ISBN 978-0-521-20095-0 , pp. 323 .


