Terevaka: Difference between revisions
Content deleted Content added
Volcanoguy (talk | contribs) removed Category:Pleistocene volcanoes; added Category:Pleistocene shield volcanoes using HotCat |
Copy edit. |
||
| Line 21: | Line 21: | ||
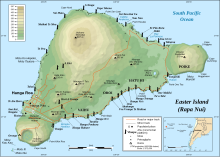
'''Ma′unga Terevaka''' is the largest, tallest ({{convert|507.41|m|ft|2|abbr=on}}) and youngest of three main [[extinct volcano]]es that form [[Easter Island]]. Several smaller volcanic cones and craters dot its slopes, including a crater hosting one of the island's three lakes, Rano Aroi. |
'''Ma′unga Terevaka''' is the largest, tallest ({{convert|507.41|m|ft|2|abbr=on}}) and youngest of three main [[extinct volcano]]es that form [[Easter Island]]. Several smaller volcanic cones and craters dot its slopes, including a crater hosting one of the island's three lakes, Rano Aroi. |
||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
While Terevaka forms the bulk of Easter Island, the island has two older volcanic peaks: [[Poike]] which forms the eastern headland and [[Rano Kau]] the southern. Terevaka last erupted in the [[Pleistocene]] and is less than 400,000 years old. Its lava field at Roiho has been dated at between 110,000 and 150,000 years old. Terevaka can be climbed via a trail that starts next to the moai at [[Ahu Akivi]]. |
While Terevaka forms the bulk of Easter Island, the island has two older volcanic peaks: [[Poike]] which forms the eastern headland and [[Rano Kau]] the southern. Terevaka last erupted in the [[Pleistocene]] and is less than 400,000 years old. Its lava field at Roiho has been dated at between 110,000 and 150,000 years old. Terevaka can be climbed via a trail that starts next to the moai at [[Ahu Akivi]]. |
||
Terevaka is the 12th most topographically isolated summit on Earth.{{refn|{{cite web|url=https://www.peakbagger.com/list.aspx?lid=302|title=World Peaks with 300 km of Isolation|website=Peakbagger.com|access-date=5 March 2020}}}} |
Terevaka is the 12th most topographically isolated summit on Earth.{{refn|{{cite web|url=https://www.peakbagger.com/list.aspx?lid=302|title=World Peaks with 300 km of Isolation|website=Peakbagger.com|access-date=5 March 2020}}}} |
||
<gallery widths=220px heights=160px> |
|||
| ⚫ | |||
| ⚫ | |||
</gallery> |
|||
==See also== |
==See also== |
||
| Line 49: | Line 50: | ||
* Kaneoka I, Katsui Y, 1985. K-Ar ages of volcanic rocks from Easter Island. Bull Volc Soc Japan, 30: 33–36. |
* Kaneoka I, Katsui Y, 1985. K-Ar ages of volcanic rocks from Easter Island. Bull Volc Soc Japan, 30: 33–36. |
||
* Vezzoli L, Acocella V, 2009. Easter Island, SE Pacific: an end-member type of hotspot volcanism. Geol Soc Amer Bull, 121: 869–886. |
* Vezzoli L, Acocella V, 2009. Easter Island, SE Pacific: an end-member type of hotspot volcanism. Geol Soc Amer Bull, 121: 869–886. |
||
{{reflist}} |
{{reflist}} |
||
==External links== |
==External links== |
||
* [http://terevaka.net/ Education-Conservation-Research] Terevaka Archaeological Outreach (non-profit) |
* [http://terevaka.net/ Education-Conservation-Research] Terevaka Archaeological Outreach (non-profit) |
||
Revision as of 01:17, 18 May 2023
| Ma′unga Terevaka | |
|---|---|
 | |
| Highest point | |
| Elevation | 1,664 ft (507 m)[1] |
| Coordinates | 27°5′4″S 109°22′46″W / 27.08444°S 109.37944°W |
| Geography | |
| Location | Easter Island |
| Geology | |
| Mountain type | Shield volcano |
| Last eruption | Pleistocene, less than 110,000 years ago |
Ma′unga Terevaka is the largest, tallest (507.41 m (1,664.73 ft)) and youngest of three main extinct volcanoes that form Easter Island. Several smaller volcanic cones and craters dot its slopes, including a crater hosting one of the island's three lakes, Rano Aroi.
While Terevaka forms the bulk of Easter Island, the island has two older volcanic peaks: Poike which forms the eastern headland and Rano Kau the southern. Terevaka last erupted in the Pleistocene and is less than 400,000 years old. Its lava field at Roiho has been dated at between 110,000 and 150,000 years old. Terevaka can be climbed via a trail that starts next to the moai at Ahu Akivi.
Terevaka is the 12th most topographically isolated summit on Earth.[2]
-
Terevaka from space with Hanga Roa above and Rano Kau at top – a west up photo from Nasa
See also
References
- Karsten M. Haase; Peter Stoffers; C. Dieter Garbe-Schönberg (October 1997). "The Petrogenetic Evolution of Lavas from Easter Island and Neighbouring Seamounts, Near-ridge Hotspot Volcanoes in the SE Pacific". Journal of Petrology. 38 (6): 785–813. doi:10.1093/petrology/38.6.785. Retrieved 2010-03-16.
- Kaneoka I, Katsui Y, 1985. K-Ar ages of volcanic rocks from Easter Island. Bull Volc Soc Japan, 30: 33–36.
- Vezzoli L, Acocella V, 2009. Easter Island, SE Pacific: an end-member type of hotspot volcanism. Geol Soc Amer Bull, 121: 869–886.
- ^ Maunga Terevaka, Chile at Peakbagger.com
- ^ "World Peaks with 300 km of Isolation". Peakbagger.com. Retrieved 5 March 2020.
External links
- Education-Conservation-Research Terevaka Archaeological Outreach (non-profit)
- Guide to Easter Island from the Easter Island Foundation
- Old photos of Rano Aroi (upper right)