Sciatic nerve: Difference between revisions
m Took out "marijuana" that was just oddly placed in the article for some stupid reason. |
|||
| Line 23: | Line 23: | ||
The nerve enters the lower limb by exiting the [[pelvis]] through the [[greater sciatic foramen]], below the [[Piriformis]] muscle. |
The nerve enters the lower limb by exiting the [[pelvis]] through the [[greater sciatic foramen]], below the [[Piriformis]] muscle. |
||
It descends midway |
It descends midway in the [[greater trochanter]] of the [[femur]] and the [[tuberosity of the ischium]], and along the back of the thigh to about its lower third, where it divides into two large branches, the [[tibial nerve|tibial]] and [[common fibular nerve|common peroneal nerves]]. This division may take place at any point between the sacral plexus and the lower third of the thigh. When it occurs at the plexus, the common peroneal nerve usually pierces the [[Piriformis]] muscles. |
||
In the upper part of its course, the nerve rests upon the posterior surface of the ischium, the [[nerve to the Quadratus femoris]], the [[Obturator internus]] and [[Gemelli]]; it is accompanied by the [[posterior femoral cutaneous nerve]] and the [[inferior gluteal artery]], and is covered by the [[Gluteus maximus]]. |
In the upper part of its course, the nerve rests upon the posterior surface of the ischium, the [[nerve to the Quadratus femoris]], the [[Obturator internus]] and [[Gemelli]]; it is accompanied by the [[posterior femoral cutaneous nerve]] and the [[inferior gluteal artery]], and is covered by the [[Gluteus maximus]]. |
||
Revision as of 23:00, 13 November 2007
| Sciatic nerve | |
|---|---|
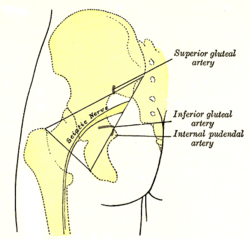 Left gluteal region, showing surface markings for arteries and sciatic nerve. | |
| Details | |
| From | lumbar plexus and sacral plexus: L4-S3 |
| To | tibial nerve, common fibular nerve |
| Innervates | Lateral rotator group (except Piriformis and Quadratus femoris), Posterior compartment of thigh |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | nervus ischiadicus |
| MeSH | D012584 |
| TA98 | A14.2.07.046 |
| TA2 | 6569 |
| FMA | 19034 |
| Anatomical terms of neuroanatomy | |
The sciatic nerve (also known as the ischiatic nerve) is a large nerve that starts in the lower back and runs through the buttock and down the lower limb. It is the longest and largest single nerve in the body.
The sciatic supplies nearly the whole of the skin of the leg, the muscles of the back of the thigh, and those of the leg and foot.
Anatomical course
The nerve enters the lower limb by exiting the pelvis through the greater sciatic foramen, below the Piriformis muscle.
It descends midway in the greater trochanter of the femur and the tuberosity of the ischium, and along the back of the thigh to about its lower third, where it divides into two large branches, the tibial and common peroneal nerves. This division may take place at any point between the sacral plexus and the lower third of the thigh. When it occurs at the plexus, the common peroneal nerve usually pierces the Piriformis muscles.
In the upper part of its course, the nerve rests upon the posterior surface of the ischium, the nerve to the Quadratus femoris, the Obturator internus and Gemelli; it is accompanied by the posterior femoral cutaneous nerve and the inferior gluteal artery, and is covered by the Gluteus maximus.
Lower down, it lies upon the Adductor magnus, and is crossed obliquely by the long head of the Biceps femoris.
Branches
The nerve gives off articular and muscular branches.
- The articular branches (rami articulares) arise from the upper part of the nerve and supply the hip-joint, perforating the posterior part of its capsule; they are sometimes derived from the sacral plexus.
- The muscular branches (rami musculares) are distributed to the following muscles of the lower limb: Biceps femoris, Semitendinosus, Semimembranosus, and Adductor magnus. The nerve to the short head of the Biceps femoris comes from the common peroneal part of the sciatic, while the other muscular branches arise from the tibial portion, as may be seen in those cases where there is a high division of the sciatic nerve.
The muscular branch eventually gives off the tibial nerve and common peroneal nerve, which innervates the muscles of the (lower) leg. The tibial nerve goes on to innervate all muscles of the foot except the extensor digitorum brevis (peroneal nerve).
Pathology
Pain caused by a compression or irritation of the sciatic nerve by a problem in the lower back is called sciatica. Common causes of sciatica include the following low back conditions: spinal disc herniation, degenerative disc disease, spinal stenosis, and spondylolisthesis.
Additional images
-
Structures surrounding right hip-joint.
-
Plan of sacral and pudendal plexuses.
-
Nerves of the right lower extremity Posterior view.
Internal links
External links
- Sciatic nerve at the Duke University Health System's Orthopedics program
- MedlinePlus Image 19503
- pelvis at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (pelvicnerves)
- glutealregion at The Anatomy Lesson by Wesley Norman (Georgetown University) (glutealner)
- Sciatica and the Sciatic Nerve - Spine-health.com
![]() This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 960 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
This article incorporates text in the public domain from page 960 of the 20th edition of Gray's Anatomy (1918)
ώ