Unit distance graph

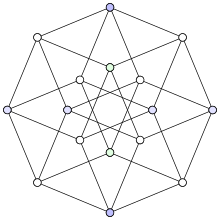
In mathematics, and particularly geometric graph theory, a unit distance graph is a graph formed from a collection of points in the Euclidean plane by connecting two points by an edge whenever the distance between the two points is exactly one. Edges of unit distance graphs sometimes cross each other, so they are not always planar.
The Hadwiger–Nelson problem concerns the chromatic number of unit distance graphs. It is known that there exist unit distance graphs requiring four colors in any proper coloring, and that all such graphs can be colored with at most seven colors.
For any algebraic number A, it is possible to find a unit distance graph G in which some pair of vertices are at distance A in any unit distance representation of G (Maehara 1991).
Examples
The following graphs are unit distance graphs:
- Any cycle graph
- Any grid graph
- Any hypercube graph
- The Petersen graph
- The wheel graph W7
Counting unit distances
How many unit distances can be determined by a set of n points?
Erdős (1946) posed the problem of estimating how many pairs of points in a set of n points could be at unit distance from each other. In graph theoretic terms, how dense can a unit distance graph be?
The hypercube graph provides a lower bound on the number of unit distances proportional to By considering points in a square grid with carefully chosen spacing, Erdős found an improved lower bound of the form
and offered a prize of $500 for determining whether or not the maximum number of unit distances can also be upper bounded by a function of this form (Kuperberg 1992). The best known upper bound for this problem, due to Spencer, Szemerédi, and Trotter (1984), is proportional to
this bound can also be viewed as counting incidences between points and unit circles, and is closely related to the Szemerédi–Trotter theorem on incidences between points and lines.
Generalization to higher dimensions
The definition of a unit distance graph may naturally be generalized to any higher dimensional Euclidean space. Any graph may be embedded as a set of points in a sufficiently high dimension; Maehara and Rödl (1990) show that the dimension necessary to embed a graph in this way may be bounded by twice its maximum degree.
See also
References
- Erdős, Paul (1946). "On sets of distances of n points". American Mathematical Monthly. 53: 248–250. doi:10.2307/2305092.
- Kuperberg, Greg (1992). "The Erdos kitty: At least $9050 in prizes!". Posting to usenet groups rec.puzzles and sci.math.
- Maehara, Hiroshi (1991). "Distances in a rigid unit-distance graph in the plane". Discrete Applied Mathematics. 31 (2): 193–200. doi:10.1016/0166-218X(91)90070-D.
- Maehara, Hiroshi; Rödl, Vojtech (1990). "On the dimension to represent a graph by a unit distance graph". Graphs and Combinatorics. 6 (4): 365–367. doi:10.1007/BF01787703.
{{cite journal}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
- Spencer, Joel; Szemerédi, Endre; Trotter, William T. (1984). "Unit distances in the Euclidean plane". Graph Theory and Combinatorics. Academic Press. pp. 293–308.
{{cite conference}}: Unknown parameter|booktitle=ignored (|book-title=suggested) (help)CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)
External links
- Venkatasubramanian, Suresh. "Problem 39: Distances among Point Sets in R2 and R3". The Open Problems Project.



