Equivalent width
The equivalent width (of English. Width ) is a measure of the astronomical spectroscopy for the strength of the lines in an absorption spectrum . It represents a quantity that does not depend on the properties of the apparatus used and is therefore well suited for comparing different measurements.
calculation
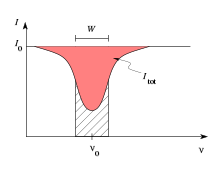
A background source of constant intensity is assumed , which is weakened by foreground material around a certain frequency .
In the intensity-frequency diagram, the strength of the absorption is given as the total area between the intensity of the background source and the actual intensity profile :
The equivalent width then corresponds to the width of a rectangle with an area equivalent to the absorbed intensity , where the height of the rectangle is given by :
units
From the calculation it can be deduced that the equivalent width is given in units of frequency (e.g. Hertz ) or in units of wavelength that is directly linked to the frequency via the speed of light (e.g. nanometers or Ångström ).
swell
- David F. Gray, The Observation and Analysis of Stellar Photospheres , Third Edition, Cambridge 2005, ISBN 0-521-85186-6