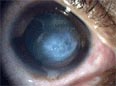
Acute keratoconus
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| H18.6 | Keratoconus |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
The acute keratoconus is a clouding of the cornea , as ophthalmological emergencies are treated immediately in an eye clinic needs.
The cloudiness can arise as a late stage of the keratoconus . Through cracks in the inner cell layer, aqueous humor can penetrate from the anterior chamber of the eye into the intercellular spaces of the cornea.
Due to the additional light scattering at the inner boundary layers of the then no longer transparent cornea, the affected person has the impression of only seeing fog . The cornea appears "milky-cloudy" from the outside and wrinkles or dents may be seen in the otherwise smooth cornea. The cornea is inflated like a balloon and the patient feels severe pain.
Some of the cracks in the cornea can widen so that aqueous humor escapes from the eye, which can also occur after mechanical injuries to the cornea.
Acute keratoconus can be confused with keratitis disciformis when viewed superficially .
literature
- Albrecht von Graefes Archive for Clinical and Experimental Ophthalmology 1979, Volume 212, Issue 2, pp 117-128: Acute keratoconus in Down syndrome