Applied image processing
Under Applied image processing refers to specific issues of image processing , such as image correction, 3D modeling , image sequence processing, and biological and medical applications.
With optical quality control in industrial production, it often happens that the segmentation has to be reset because a new batch of components with different properties is being delivered. If the measuring point is not shielded from daylight and there is no local lighting, the function of the measuring machine can be impaired by the time of day / time of year. This affects the production process, because after each adjustment the measuring capability of the optical machine has to be proven in a complex manner. And because the developers of optical machines have no influence on the suppliers of their customers, this problem can only be solved with improved image processing algorithms or new methods.
Everyone who is active in the field of optical quality control and 3D measurement is confronted with these problems, and many developers may also know that this problem can be solved with adaptive image processing.
Adaptive image processing
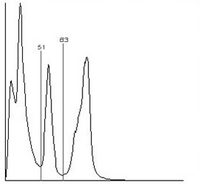
For image processing that is adaptive to lighting, an image analysis tool can be used that provides optimal thresholds of segmentation. This tool uses the histogram of the color distribution in Figure 1 to determine the threshold.
The picture shows a histogram of the gray value distribution with two useful thresholds for image processing. If light features are segmented, the second threshold is used, and in dark features the first threshold is used.
Because the threshold determination depends on the temporary histogram and is re-determined before each segmentation (for the current situation), image processing that is adaptive to the lighting is obtained.
However, there are limits to the histogram algorithms used in adaptive image processing, for example if there is only one maximum in the histogram, as in Figure 2,
the image processing adaptive to the lighting works as long as the searched feature is still sufficiently large. This corresponds to a feature area of approx. 5% and more of the entire image. Image processing that is adaptive to lighting can therefore be implemented very easily. But it is only that simple with optical measurements with uniform lighting. If this is not the case, other methods must be used.
Original image processing algorithms have been developed for such cases, which do not require any thresholds in the segmentation and find practically every feature in the image.
literature
- Joachim Ohser: Applied image processing and image analysis. Fachbuchverlag Leipzig, Munich 2018, ISBN 978-3-446-44933-6 .
Web links
- Applied sensors (accessed on July 9, 2018)