Appel reaction
The Appel reaction is a nucleophilic substitution reaction of the type S N 2, in the organic chemistry , the conversion of alcohols into the corresponding alkyl halides allows. Primary and secondary alcohols are preferably used. The Appel reaction is a special case of redox condensation according to Mukaiyama. The name reaction is named after its discoverer Rolf Appel (1921–2012, University of Bonn ), who published his research results from 1975 onwards.
Overview reaction
As reagents are stoichiometric amounts of triphenylphosphine (TPP = PPh 3 ), and a carbon tetrahalide such as carbon tetrachloride (CCl 4 ) or carbon tetrabromide (CBr 4 ) is required. The reaction cannot be carried out with tetrafluoromethane (CF 4 ).
The product of the Appel reaction is a haloalkane , in the example a chloroalkane, from an alcohol (R 1 and R 2 are organic radicals ) .
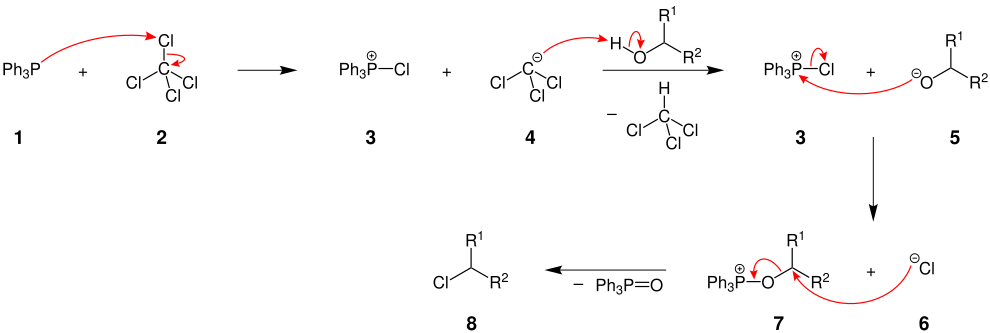
Reaction mechanism
The mechanism of the Appel reaction is described here using the example of the conversion of triphenylphosphine, carbon tetrachloride and a secondary alcohol. The radicals R 1 and R 2 are organic radicals :
The triphenylphosphine ( 1 ) is activated by the carbon tetrachloride ( 2 ) and the chlorotriphenylphosphine ( 3 ) and a deprotonated chloroform ( 4 ) are formed. The deprotonated chloroform ( 4 ) attacks the alcohol , creating an alcoholate 5 . Then the reaction between the triphenylphosphine ( 3 ) and the alcoholate 5 takes place . The molecule 7 is formed and a chloride ion is split off from the chlorotriphenylphosphine ( 3 ). In the last step, triphenylphosphine oxide is displaced as a very good leaving group by the nucleophilic attack of the chloride ion 6 and the desired product, in this case a chloroalkane 8 . The driving force of the reaction is the formation of the O = P double bond, i.e. the oxidation of P (III) to P (V).
The Appel reaction is a mild and modern variant of chlorination or bromination under S N 2 conditions. It is therefore stereoselective with inversion of configuration .
Practical meaning
The Appel reaction is a purely laboratory process. Because of the formation of stoichiometric amounts of triphenylphosphine oxide and other waste materials , the atom economy of the Appel reaction is so bad that nobody realizes an industrial synthesis for a haloalkane based on this reaction.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Reinhard Brückner: reaction mechanisms: organic reactions, stereochemistry, modern synthesis methods . 3. Edition. Springer, 2004, ISBN 3-662-45683-4 , pp. 99 .
- ↑ a b Appel reaction. Retrieved August 9, 2019 .
- ^ Z. Wang: Comprehensive Organic Name Reactions and Reagents, 3 Volume Set , there in Volume 1, John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken, New Jersey 2009, ISBN 978-0-471-70450-8 , p. 95.
- ^ Substitution reactions on aliphatics . EPF Lausanne, accessed on November 2, 2011.
literature
- Rolf Appel: Tertiary Phosphane / Tetrachloromethane, a Versatile Reagent for Chlorination, Dehydration, and P – N Linkage. In: Angewandte Chemie International Edition in English. 14, No. 12, 1975, pp. 801-811, doi : 10.1002 / anie.197508011 .