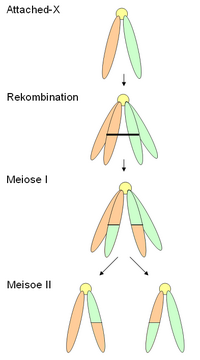
Attached X chromosome
In so-called Attached X-chromosomes is specific X chromosomes of Drosophila , in the centromere are fused together. Therefore, these two chromosomes behave as a single one (for example during the distribution during mitosis and meiosis ), but represent a diploid state. This special behavior offers one of the few possibilities in higher eukaryotes to directly investigate the effects of recombination during meiosis.
Since the two chromosomes are not separated after a recombination within the attached X chromosome (no reduction division ), the result of the recombination can be read directly in the resulting germ cells if one arm contained marker genes. From the results of these observations it was concluded that the recombination must take place in the bivalent .
Individual evidence
- ↑ MM Green, R. Piergentili: On the origin of metacentric, attached-X (AX) chromosomes in Drosophila melanogaster males. In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences . Volume 97, Number 26, December 2000, pp. 14484-14487, ISSN 0027-8424 . doi : 10.1073 / pnas.250483497 . PMID 11106377 . PMC 18945 (free full text).