Rail engine
When traction motor is a universal motor , which is optimized for use on a traction unit, designated. Until around 1980 it was practically the only engine used on electric traction vehicles.
Structure, function and use
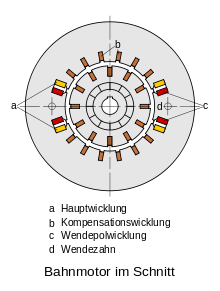
Large single-phase series motors with reversing pole and compensation windings are used as traction motors for electric locomotives . These motors have outputs of up to 1000 kilowatts and, in contrast to the repulsion motor, can be operated with direct current , alternating current and mixed current . The control (i.e. voltage control for speed setting ) takes place depending on the respective traction current system via a variable transformer (at 16 2/3 Hertz), series resistors (for DC systems) or via rectifiers (at 50 and 60 Hertz ).
The term rail engine is fundamentally different from the term traction engine . While traction motor refers to all types of motors used on electric traction vehicles, rail motor refers exclusively to the single-phase series motor .
Due to the improved power electronics, the single-phase commutator motors ( repulsion motor , single-phase series motor ), as railway motors, are gradually being replaced by three-phase motors in combination with frequency converters .
literature
- Ernst Hörnemann, Heinrich Hübscher: Electrical engineering specialist training in industrial electronics. 1st edition. Westermann Schulbuchverlag GmbH, Braunschweig, 1998, ISBN 3-14-221730-4
- Hans Günter Boy, Horst Flachmann, Otto Mai: The master's degree in electrical machines and control technology. 4th edition, Vogel Buchverlag, Würzburg, ISBN 3-8023-0725-9
- Detlev Roseburg: Electrical machines and drives. Fachbuchverlag Leipzig in Carl Hanser Verlag, 1999, ISBN 3-446-21004-0