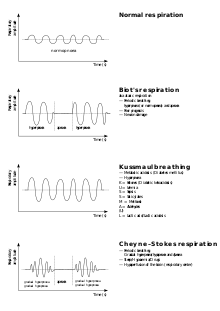
Biot breathing
As Biot's respiration (rare: meningitisches breathing or ataxic respiration ) is a form of periodic or intermittent breathing called, are repeatedly interrupted by sudden pauses in sufficiently strong and uniform deep breaths. This form of breathing indicates a serious impairment of the respiratory center . This breathing disorder is named after the French doctor Camille Biot (1850–1918).
causes
Biot breathing is typical for damage to the respiratory center in the medulla oblongata , part of the brain stem. The nerve cells involved are part of the reticular formation that occurs in this part of the brain . Biot breathing occurs in the context of increased intracranial pressure , meningoencephalitis and direct damage in this area, such as through brain contusion .
Occasionally, it can also occur in healthy premature and newborn babies .
See also
- Respiratory drive
- Cheyne-Stokes breathing
- Hyperventilation
- Hypoventilation
- Kussmaul breathing
- Pathological form of breathing
Individual evidence
- ↑ Stefan Schwab u. a .: Neurological intensive care medicine. Springer, Berlin 1999, ISBN 3-540-65412-7 , p. 895.
- ↑ EF Wijdicks: Biot's breathing . In: J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatr. tape 78 , no. 5 , May 2007, pp. 512-513 , doi : 10.1136 / jnnp.2006.104919 , PMID 17435185 .
- ↑ a b Wolfgang Oczenski: Breathing breathing aids. Respiratory physiology and ventilation technology. Georg Thieme Verlag, 2008, ISBN 978-3-13-137698-5 , p. 129.