Premature birth
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| P07.2 | Newborn with extreme immaturity
Gestational age less than 28 completed weeks (less than 196 days) |
| P07.3 | Others born before the appointment
Gestational age of 28 or more completed weeks, but less than 37 completed weeks (from 196 completed days to less than 259 completed days) |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
From a premature birth is called in the birth of an infant before the age of 37. week of pregnancy ( SSW ). Sometimes those affected are also referred to as premature births (even for life); their property is called prematurity . A typical pregnancy lasts 40 weeks (280 days after the last menstrual period ). In premature babies - often called "premature babies" - it lasts less than 260 days; counted from the first day of the last menstruation . They usually weigh less than 2500 grams.
The earliest survivor in Europe born until 2010 was born after just 152 days (21 weeks and five days) and weighed 460 g and was 26 cm tall. In December 2018, Saybie was born in the Sharp Mary Birch Hospital in San Diego with a weight of almost 245 g as the world's lightest surviving newborn child after induction in the 23rd week of pregnancy.
According to a recent study by the WHO , one in ten babies worldwide is born prematurely. The number is increasing in almost all countries. This also applies to industrialized nations, which is due to the increasing age of the mothers at birth. In Germany, the premature baby rate is 9.2%. Around 63,000 children are born before the 37th week of pregnancy in Germany each year. 8,000 of them are premature babies born before the 30th week of pregnancy.
Premature births are the subject of neonatology , a branch of pediatrics (pediatrics).
Terms
Very small premature babies (VLBW = Very Low Birth Weight ) are babies who weigh less than 1500 grams and are usually less mature than 32 weeks of gestation, while extremely small premature babies (ELBW = Extremely Low Birth Weight ) are babies with a birth weight of less than 1000 grams.
In premature babies, a distinction is also made between babies who are unusually small and unusually light for the duration of pregnancy ( gestational age ). These are called hypotrophic premature babies or small-for-gestational-age babies ( SGA babies ). In addition, there are premature babies who are unusually large and unusually heavy for the duration of pregnancy ( gestational age ). They are called hypertrophic . They are also called large-for-gestational-age babies ( LGA babies ).
causes
In many cases, the exact cause of the premature labor and / or premature rupture of the bladder that lead to premature birth cannot be found. Possible triggers are described in the literature for either maternal, fetal or socio-economic reasons.
The most common cause is urogenital infections in the mother. Pregnancy complications (e.g. placental insufficiency , anemia or gestosis ) can also cause premature birth. In addition, psychosocial triggers are mentioned. This includes, for example, chronic stress from multiple work, family and household loads.
Some studies indicate that undiagnosed or untreated celiac disease (synonyms: indigenous celiac disease , gluten-sensitive enteropathy) can also be responsible for premature births and other problems during pregnancy and in this context is still an underestimated cause. In more recent studies it has also been shown that periodontitis can also be a cause of premature births and / or a low birth weight. Smoking before and during pregnancy can trigger premature births. An international study by the World Health Organization (2014) shows that smoking bans in public buildings (which probably also include workplaces) in Europe and North America have significantly reduced the number of premature births in these countries.
According to a Swedish study, bariatric surgery favor later premature births and a low birth weight. The reason for this can be a shortage of nutrients in the fetus due to a smaller stomach or a shortened intestine.
In addition to triggers on the part of the mother, there can also be causes that emanate from the fetus itself. These include malformations, chromosomal abnormalities, multiple pregnancies or rhesus incompatibility .
The heat exposure in the context of the climate crisis also increases the risk of childbirth for pregnant women. This results in a shorter pregnancy, which can lead to health and cognitive problems for the child later. Based on a comparison of birth rates and weather data in the United States from 1969 to 1988, the pregnancy problems associated with heat could be quantified. Extreme heat caused an increase in the number of births on the day of heat exposure and the following day and additional births were accelerated by up to two weeks. It is estimated that an average of 25,000 infants per year were born prematurely due to exposure to heat, with a total loss of more than 150,000 gestational days per year. Climate projections indicate additional losses of 250,000 gestational days per year by the end of the century.
Problems of the premature baby
The immature organs lead to various problems. The extent of lung maturity is particularly important and crucial for survival.
Respiratory distress syndrome, IRDS (infant respiratory distress syndrome), surfactant deficiency syndrome
→ Main article: Newborn respiratory distress syndrome
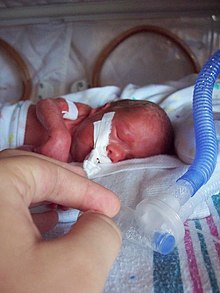
The immature lung produces only a small amount of surfactant in an IRDS . This causes the alveoli to collapse, which then cannot participate in gas exchange. Oxygen deficiency and shortness of breath are the consequences. In the collapsed alveoli to blood proteins accumulate, and there are for IRDS typical hyaline membranes. For treatment, the premature baby is intubated and artificially ventilated . Surfactant can be introduced into the lungs via the ventilation hose. As a preventive measure, corticosteroids , which promote lung maturity, can be given before birth .
Kidney failure
The immature kidney does not produce urine . Therefore, substances accumulate in the blood that would otherwise be excreted in the urine. Among these, potassium is of particular importance, as an increased potassium level in the blood ( hyperkalaemia ) can lead to life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias . The two post-kidneys take up their function at the beginning of the second half of pregnancy; the glomeruli produce the primary urine , the tubules secrete the secondary urine . The drunk amniotic fluid is excreted again. Also embryos and fetuses without kidneys (bilateral renal agenesis ) or non-functioning kidney (absolute kidney failure ) develop normally until birth because they their uremic substances through the placenta into the maternal Make circulation. Before giving birth , the placenta functions as a kind of kidney dialysis , regardless of health or illness. The glomerular filtration rate of 1 kg premature babies is 0.2 ml / min. This renal insufficiency is physiological in premature babies and also in mature newborns .
Cerebral hemorrhage
For intracerebral hemorrhage occurs in premature babies particularly under a gestational age of 32 + 0 weeks of pregnancy. With increasing immaturity, the risk increases. The risk of high-grade bleeding (see below) in Germany is around 5–6% for children <32 weeks of pregnancy and around 25% for children <26 weeks of pregnancy. A collection of small vessels (germinal matrix), which is located below the two lateral ventricles (inner cerebral water spaces), is particularly critical in premature babies. These vessels can tear, assisted by various factors. This causes bleeding. Slight bleeding (grade 1) remains localized. A mild bleeding (grade 2) pours into the cerebral water spaces of the lateral ventricles and fills them up to 50%. Severe bleeding (grade 3) fills the lateral ventricles to over 50%. If the bleeding leads to an obstruction of the draining veins leading through the area of the small vessels (germinal matrix), this can lead to further severe bleeding in the nerve tissue of the brain (previously: grade 4). Grade 1 and Grade 2 bleeding have a favorable prognosis. From a grade 3 bleeding onwards, disabilities are to be expected (mainly motor). In the case of acute bleeding, the loss of blood can lead to shock ; in the further course the blood can obstruct the drainage of the cerebral fluid . A hydrocephalus is the result.
The administration of platelets is discussed to reduce the risk of bleeding . With a normal platelet count in the blood of the premature infant, no improvement could be achieved with a platelet transfusion. However, 73% of all children with a birth weight of less than 1000 g develop thrombocytopenia during their stay in the neonatal ward. In the case of thrombocytopenia with less than 50,000 platelets per mm 3 of blood, the administration of platelet concentrate is recommended. However, the data situation is contradictory.
Necrotizing enterocolitis
The bowel movements ( peristalsis ) are not yet regular in premature babies. It can build up in the intestines. Bacteria grow in this environment and can be a cause of the intestinal inflammation, necrotizing enterocolitis (NEC). In the X-ray image of air bubbles can be seen in the intestinal wall ( pneumatosis intestinalis ) . When the intestine ruptures , air enters the abdominal cavity .
Persistent ductus arteriosus
The patency of the ductus arteriosus after birth ( Patent ductus arteriosus , PDA) leads the child's blood circulation disturbances. When the partial pressure of oxygen is increased, the muscle cells of the ductus arteriosus contract, which normally causes the vessel to close. If hypercapnia , hypoxia and respiratory acidosis occur in a depressed premature infant , the contraction stimulus is not given. As a result, the left-right shunt persists and pulmonary hypertension continues , which worsens the clinical picture. The whole thing is circular and has to be broken therapeutically.
Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) in premature infants
The retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) is a disease of the retina , which is due to an excessive formation of blood vessels to retinal detachment may occur. Timely therapy using laser treatment or injection of VEGF blockers such as ranibizumab and bevacizumab can usually stop the disease process and prevent blindness.
Immature immune system
Premature babies have an imperfectly developed immune system , with both innate and adaptive immune responses being reduced. In addition, the immune system can be damaged by other effects of early birth.
forecast
Today, the completion of the 23rd week of pregnancy is considered a necessary condition for the survival of a premature baby with medical help. However, mortality and morbidity are particularly high in very immature infants and depend heavily on the experience of the treating medical team.
- In 2002 a girl was born in the Helios Clinic in Erfurt in the 25th week of pregnancy. It weighed 350 grams at birth, but at the age of six showed almost no developmental deficits.
- In 2006, a girl was born in a clinic in Miami in the 22nd week of pregnancy and weighed 280 g and was 24 cm tall.
- In 2009, a boy with a birth weight of 275 grams, who was born in the 25th week of pregnancy, was kept alive at the Göttingen University Hospital .
- In 2010 a girl named Frieda survived in Fulda , who was born after 21 weeks and 5 days weighing 460 grams.
- In 2011, a girl survived in the Greifswald University Children's Hospital ( Neonatology Department ) who was born in the 22nd week weighing 490 grams and initially lost 90 grams before gaining weight. With babies this small, the equipment (for example ventilation technology ) reaches its limits.
- In 2011, a girl at the Helios Klinikum Berlin-Buch survived who was born in the 24th week weighing 400 grams, although the small intestine was perforated after the birth .
- In 2014, a girl survived at the Methodist Children's Hospital in San Antonio (Texas / USA) who was born after 21 weeks and 4 days with a weight of 410 grams. It was just as developed by the age of three as other children her age.
- In 2019, a girl named Melina survived at the Fulda Clinic , who was born after 21 weeks and 4 days. The twin brother died a few hours after the birth.
Probability of survival
The probability of survival depends strongly on the respective gestational age . The data suggest that the limit of viability is between the 22nd and 24th week of pregnancy. The main reason for this is the lack of lung maturity , as this organ does not develop fully until relatively late and is essential for survival. For children born in the 24th and 25th week of pregnancy, the probability of survival has leveled off at around 70–85% as a result of advances in caring for immature premature babies. The probability of survival increases with each additional week, at 28 and 29 weeks of pregnancy it is already over 90%.
Very small premature babies with a birth weight of <500 g have a poor chance of survival regardless of maturity. In Germany it is currently around 20 to 30%.
Over a million children worldwide die annually as a result of their premature birth . This makes it the most common cause of death in newborns and the second most common cause of death in children under the age of five, after pneumonia .
Therapy for extremely premature children costs around 90,000 euros in Germany (as of 2012).
Long-term consequences
Due to various medical and technical advances, the number of children who survive a birth that is considerably premature is increasing. But the more immature a child is born, the higher the risk of permanent physical handicap or cognitive impairment. The risk of attention deficit / hyperactivity disorder is also increased by premature birth, regardless of genetic disposition . In an average of four out of five children born before the 26th week of pregnancy, damage can be detected at the age of six, which can clearly be attributed to the unusually early birth.
Studies indicate that, in the long term, children who weighed less than 1,000 grams at birth are more likely to develop health problems than other children: an American study that examined 219 premature children aged eight years found 21 % Asthma diseases (as opposed to 9% in the control group), in 47% motor disorders (as opposed to 10% in the control group) and in 38% an intelligence quotient of less than 85 (as opposed to 15% in the control group). Another study showed statistically that premature men and women have fewer offspring. In premature women, there is also an increased risk of having a premature birth themselves.
25% of all extremely premature births (birth weight <1,000 g) show signs of autism in childhood . One or more learning disabilities (such as reading and writing difficulties and / or arithmetic weaknesses ) are also much more common in extremely premature babies than in full term babies. According to US statistics, every second premature baby with a birth weight of less than one kilogram is learning disabled by the age of eight. The reduced intelligence was also confirmed in a recent American study, according to which premature birth should be responsible for 15% of all intellectual disabilities. Other mental disorders (such as depression and anxiety disorders ) and behavioral disorders are also more common in extremely premature babies.
Measures in the event of impending premature birth
In the event of an impending premature birth, measures are usually taken to support the child's lung maturation : By giving the mother prenatal glucocorticoids ( cortisone , betamethasone ), the formation of the surfactant in the child's lungs is stimulated. Surfactant is a mixture of phospholipids and proteins , which is necessary for the development of the lungs by reducing the surface tension in the alveoli .
Treating clinics and perinatal centers
In many industrialized countries, the treatment of critical premature births before the 26th week of pregnancy is only carried out in special perinatal centers , which must have a certain number of cases. In Germany, in December 2008 the responsible federal committee of doctors, hospitals and health insurance companies ordered that at least twelve cases of premature babies per year must be treated in specialized hospitals. Up to 80 of the previous 400 clinics are no longer offering premature baby care. In February 2009, the panel also decided that the treating hospitals must publish the mortality rate and frequency of complications on the Internet.
It has been scientifically proven that there is a direct relationship between the number of high-risk births before the 26th week of pregnancy in a clinic and the success of treatment: the more experienced the doctors and the higher the number of cases, the greater the chance of the child surviving without long-term consequences.
This is clearly shown by a medical study from 2006 based on statistics on premature babies in Baden-Württemberg in 2003/2004. It compares the mortality rate of the five largest perinatal centers (Freiburg, Heidelberg, Tübingen, Ulm and Stuttgart) with that of all other clinics. For premature babies born before the 26th week of pregnancy, the mortality rate was 15% in the centers mentioned, compared with 33% in the other hospitals. From the 26th week of pregnancy, however, the statistics no longer differ significantly.
Media reception
Every year in Germany, 8,000 premature babies are born weighing less than 1,500 grams. It is widely reported in the media.
The development of neonatal intensive care medicine, which began around 1975, was initially hardly noticed by the public. Otwin Linderkamp (University of Heidelberg) wrote in 1994:
“For some years now, the media have been reporting more and more frequently about premature babies, but mostly focus on the risk of disabilities. Many reports claim that most extremely immature infants with severe disabilities survive. Nurses and doctors who work in neonatal intensive care units are often subjected to pressures to justify their actions that other areas of medicine hardly know. However, this has also contributed to the fact that neonatal research is making every effort to further reduce the risk of permanent damage in premature infants, especially brain damage. At the same time, all those involved try to provide the infants with the most humane and gentle care possible, despite the necessary technology. "
See also
literature
- Friedrich H. Steeg: Connection between premature birth and poor numeracy? In: The premature child. e. V., 4/2004: [partial service disruptions]
- Association for the promotion of premature and high-risk babies “Das Frühchen” e. V. Heidelberg (ed.): Everything turned out very differently; A book for parents who received a premature baby. Heidelberg 2000, ISBN 3-00-007070-2 .
Web links
- Familienplanung.de - Premature birth : The information portal of the Federal Center for Health Education (BZgA)
- Federal Association "The Premature Child" e. V. Umbrella organization of the parents' initiatives and support associations for premature babies and sick newborns.
- The European Foundation for the Care of Newborn Infants (EFCNI) is a non-profit foundation that, as the umbrella organization of the European parents' associations for premature babies and sick newborns, creates networks of parent representatives, experts and politicians with the aim of improving care in Europe.
- S2k guidelines for the prevention and treatment of premature birth from the DGGG, OEGGG and SGGG. In: AWMF online (as of February 2019)
- S2k guideline Idiopathic apneas, bradycardia and hypoxemia in premature infants, therapy of the Society for Neonatology and Pediatric Intensive Care Medicine and the German Society for Pediatrics and Adolescent Medicine. In: AWMF online (as of April 2014)
- S2k guideline for premature babies at the limit of viability of the German Society for Gynecology and Obstetrics a. a .. In: AWMF online (as of April 2014)
- The premature baby portal The information portal for high-risk pregnancy and premature birth for parents / relatives and the professional groups involved
Individual evidence
- ↑ Jörn Perske: 21-week premature baby Frieda is awake. In: welt.de . March 1, 2014, accessed February 2, 2015 .
- ↑ "Lightest baby in the world leaves clinic", in: Frankfurter Allgemeine Zeitung for Germany, number 125/2019, May 31, 2019, p. 6.
- ^ "Baby survives with only 245 grams", dpa report in: Neue Westfälische , Bielefelder Tageblatt , 209th year, number 126/2019, 1st / 2nd June 2019.
- ↑ who.int
- ↑ hil / aerzteblatt.de: More than 15 million premature babies worldwide - and the trend is rising. In: aerzteblatt.de . May 3, 2012, accessed February 2, 2015 .
- ↑ Premature babies: 8,000 births before the 37th week of pregnancy. In: aerztezeitung.de. November 14, 2012, accessed February 2, 2015 .
- ↑ J. Steidinger, KJ Uthike: Premature babies - From babies who cannot wait. Rowohlt, Hamburg 1995, ISBN 3-499-18504-0 .
- ↑ M. Glöckner: Medical Actions in Extremely Immature Babies: Legal and Ethical Aspects. Springer, 2007.
- ↑ a b C. Mändle, S. Opitz-Kreuter: Das Hebammenbuch: Textbook of practical obstetrics. 5th edition. Schattauer Verlag, 2007.
- ↑ P. Martinelli include: Celiac disease and unfavorable outcome of pregnancy. In: Gut, BMJjournals. 2000, 46 (3), pp. 332-335. PMID 1727862
- ↑ C. Ciacci et al: Celiac disease and pregnancy outcome. In: Am J Gastroenterol . 1996, 41 (5), pp. 972-978. PMID 8625771
- ↑ International study: Smoking bans lead to fewer premature births. on: spiegel.de , March 28, 2014.
- ^ Effect of smoke-free legislation on perinatal and child health: a systematic review and meta-analysis. In: The Lancet . March 28, 2014.
- ↑ N. Roos, M. Neovius, p Cnattingius, Y. trolls Lagerros, M. Saaf, F. Granath, O. Stephansson: Perinatal outcomes after bariatric surgery: nationwide population-based matched cohort study. In: BMJ. 347, 2013, pp. F6460 – f6460, doi: 10.1136 / bmj.f6460 .
- ↑ See also Arthur Hoffmann: On the initiation of artificial premature birth through hot full baths. In: Centralblatt für Gynäkologie. Volume 10, No. 32, August 7, 1886, pp. 513-515.
- ↑ Barreca, A., Schaller, J. The impact of high ambient temperatures on delivery timing and gestational lengths. Nat. Clim. Chang. (2019) doi: 10.1038 / s41558-019-0632-4
- ^ Jan Langman: Medical Embryology , 5th edition, Thieme-Verlag , Stuttgart 1977, ISBN 3-13-446605-8 , p. 175.
- ↑ Jürgen Sökeland: Urology , 10th edition, Thieme-Verlag , Stuttgart, New York 1987, ISBN 3-13-300610-X , p. 4.
- ^ Markus Daschner: Tabellarium Nephrologicum , 3rd edition, Shaker Verlag , Aachen 2009, ISBN 978-3-8322-7967-7 , p. 67.
- ↑ (Hessian Neonatal Survey 2005)
- ↑ (Source: including Volpe: Neurology of the Newborn)
- ^ M Andrew, P Vegh, C Caco, H Kirpalani, A Jefferies: A randomized, controlled trial of platelet transfusions in thrombocytopenic premature infants . In: The Journal of Pediatrics . tape 123 , no. 2 , 1993, ISSN 0022-3476 , pp. 285-291 , PMID 8345429 .
- ↑ RD Christensen, E Henry, SE Wiedmeier, et al .: Thrombocytopenia among extremely low birth weight neonates: data from a multihospital healthcare system. In: Journal of Perinatology . tape 26 , 2006, p. 348-353 .
- ↑ Anna Curley, Simon J. Stanworth, Karen Willoughby, Susanna F. Fustolo-Gunnink, Vidheya Venkatesh: Randomized Trial of Platelet-Transfusion Thresholds in Neonates . In: New England Journal of Medicine . tape 380 , no. 3 , January 17, 2019, ISSN 0028-4793 , p. 242-251 , doi : 10.1056 / NEJMoa1807320 ( nejm.org [accessed February 28, 2019]).
- ↑ Martha C. Sola Visner: Platelet Transfusions in Neonates - Less Is More . In: New England Journal of Medicine . tape 380 , no. 3 , January 17, 2019, ISSN 0028-4793 , p. 287–288 , doi : 10.1056 / NEJMe1813419 ( nejm.org [accessed February 28, 2019]).
- ^ DJ Schneider, JW Moore: Patent ductus arteriosus. In: Circulation. 114 (17), Oct 24, 2006, pp. 1873-1882. Review. PMID 17060397
- ↑ Retinopathy of premature infants: Update on pathogenesis, screening and new therapy options . The Ophthalmologist , December 2012 edition (pdf; 2.2 MB).
- ↑ Jacqueline M. Melville, Timothy JM Moss: The immune consequences of preterm birth. In: Frontiers in Neuroscience. 7, 2013, S., doi: 10.3389 / fnins.2013.00079 .
- ↑ Malte Wicking: Premature births can be avoided . Interview with Clinic Director Professor Udo Hoyme, Senior Physician Silke Meinig and Senior Physician Lutz Braun from the Perinatal Center in the Erfurt Helios Clinic in the Thüringer Allgemeine , March 17, 2010, accessed on May 30, 2016.
- ↑ Premature births can be avoided | Health & Medicine | Thuringian General. February 18, 2020, accessed July 31, 2020 .
- ↑ Most-premature baby allowed home . BBC , February 21, 2007, accessed May 30, 2016.
- ↑ A handful of baby. Fruehchen with a birth weight of 275 grams survived. In: Osnabrück newspaper.
- ↑ Europe's youngest premature baby discharged from the clinic. on: focus.de
- ↑ MEDIA INFORMATION. Greifswald, September 24, 2011 ( Memento of the original from December 12, 2013 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice. (pdf; 84 kB)
- ↑ Helena is Berlin's smallest miracle. In: Bild newspaper
- ↑ Mom pleads with doctor to resuscitate baby delivered at 21 weeks. 'Miracle' daughter is now a healthy toddler . In: USA TODAY . ( usatoday.com [accessed January 3, 2018]).
- ↑ sensation! The world's youngest premature baby released from the Fulda Clinic. May 30, 2020, accessed on May 31, 2020 (German).
- ↑ D. Singer: Long-term survival of premature infants. In: Federal Health Gazette. 55, 2012, pp. 568-575.
- ↑ who.int
- ↑ What health costs. In: fit! No. 4, 2013, ( PDF file ( Memento from December 12, 2013 in the Internet Archive )), p. 25.
- ↑ Apothekenumschau. 10/2005, p. 67.
- ↑ Early birth, late consequences . In: Wissenschaft.de. March 26, 2008, accessed September 8, 2019 .
- ^ Childhood Autism Linked To Substantial Loss Of Household Income. ( Memento from April 25, 2011 in the web archive archive.today ) on: aap.org , April 2008.
- ↑ High rate of autism signs found in children born extremely prematurely, researchers find. ( Memento from April 6, 2008 in the web archive archive.today ) at: startribune.com , April 2008.
- ↑ archpedi.ama-assn.org
- ↑ archpedi.ama-assn.org
- ↑ JP Brosco, LM Sanders, M. Dowling, G. Guez: Impact of specific medical interventions in early childhood on increasing the prevalence of later intellectual disability . In: JAMA Pediatrics . tape 167 , no. 6 , June 1, 2013, p. 544-548 , doi : 10.1001 / jamapediatrics.2013.1379 .
- ↑ health.am
- ↑ theage.com.au
- ↑ scienceblog.com
- ↑ medscape.com ( Memento of the original from October 18, 2002 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ↑ Hospitals: Born in the Wrong Place. In: Der Spiegel. 44/2007, October 29, 2007.
- ↑ HD Hummler, C. Poets, M. Vochem, R. Hentschel, O. Linderkamp: Mortality and morbidity of very immature babies in Baden-Württemberg as a function of the size of the clinic. Is the current degree of regionalization sufficient? In: Z Obstetrics Neonatol. 210, 2006, pp. 6-11. doi: 10.1055 / s-2006-931508
- ↑ a b A chance for lightweights. In: UniSpiegel. 1/1994.