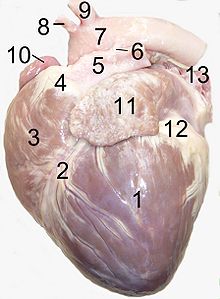
Ductus arteriosus
The ductus arteriosus (also called Ductus arteriosus Botalli , Ductus Botalli or Ductus arteriosus Harvey ) is the vascular connection between the aorta (the main artery ) and the pulmonary trunk (pulmonary artery) in the fetal (prenatal) bloodstream . Since the lungs are not yet ventilated and therefore not yet relevantly supplied with blood, the blood flows via the ductus arteriosus from the pulmonary artery directly into the aorta.
Prenatal Development
The ductus arteriosus arises in the embryo from the left 6th branchial arch artery .
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs), such as B. ibuprofen , can lead to premature closure of the fetal ductus arteriosus in the course of prenatal (prenatal) development, as its sensitivity increases with increasing gestational age .
Postnatal Development
The ductus arteriosus closes ( obliterated usually) in the first days of life to -weeks after birth ( postnatal ) and forms the arteriosum ligament , which as connective tissue of the pulmonary trunk to the aortic arch connects. This process is triggered by a postnatal increase of the oxygen - partial pressure (pO 2 ) at the onset of respiration. The intima of the duct proliferates and the smooth muscles actively contract . If the physiological obliteration of the ductus arteriosus does not occur, one speaks of a persistent ductus arteriosus .
In connection with various complex congenital heart defects , however, a ductus arteriosus is artificially kept open by the administration of prostaglandins in order to ensure the survival of the children. For example, in the case of a transposition of the great arteries (TGA), the body and pulmonary circulation are separated. An open ductus arteriosus (or an open foramen ovale ) is the only way to distribute the oxygenated blood in the lungs throughout the body.
Another connection between the pulmonary circulation and the body circulation in the fetal circulation is the foramen ovale , which represents an opening between the right and left atrium and closes postnatally to the structure visible in the right atrium as the oval fossa.
History of exploration
The ductus arteriosus was already described by Galen , but its importance was only recognized by William Harvey in 1628 . The fact that the discovery was wrongly assigned to Leonardo Botallo was due to a translation error by Van Hornes, who in 1680 produced a collective edition of Botallo's works.
The first successful closure of a persistent ductus arteriosus was achieved in 1938 by Gross and Hubbard.
Individual evidence
- ↑ embryotox.de ( Memento of the original from January 24, 2012 in the Internet Archive ) Info: The archive link was inserted automatically and has not yet been checked. Please check the original and archive link according to the instructions and then remove this notice.
- ^ A b Jürgen Apitz (Ed.): Pediatric Cardiology. Heart diseases in newborns, infants, children and adolescents. Steinkopff, Darmstadt 1998, ISBN 3-7985-1036-9 , p. 380.
literature
- Douglas J. Schneider, John W. Moore: Patent ductus arteriosus. In: Circulation . Vol. 114, No. 17, 2006, pp. 1873-1882, doi: 10.1161 / CIRCULATIONAHA.105.592063 , PMID 17060397 .