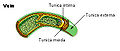
Tunica intima

The tunica intima (from Latin tunica = "garment" and intimus "the innermost"), also called tunica interna (from Latin interna = "the inside", "inside"), is the inner layer of the blood and Lymphatic vessels .
construction
- The endothelium is a monocellular layer and is in direct contact with the blood. Endothelial cells are flattened and polygonal . Your cell nucleus bulges into the lumen .
- Subendothelial connective tissue layer
- Internal elastic membrane; Elastic fibers condensed into a windowed layer
Outwardly, viewed from the lumen, the tunica intima borders the tunica media .
function
In order to enable the best possible blood flow, the endothelial cells ensure a smooth inner surface. The surface facing the lumen usually repels solid blood components such as red blood cells and leukocytes . However, erythrocytes, for example, can attach to a damaged endothelium. So among other things with an inflammation . The cell adhesion molecules then produced by the endothelium allow other cells to adhere to the wall of the blood vessel.
The endothelium also represents a selectively permeable barrier for dissolved blood components. In addition, it releases substances that have a vasoconstrictor and vasodilator effect, such as nitrogen monoxide (NO).
The mean thickness of the tunica interna can be between 7 and 140 µm, depending on the blood vessel.
The endothelium controls the interactions with the blood and the surrounding tissue itself. The most important functions are the regulation of the vascular wall tone , the antithrombogenic effect and the control of exchange processes. The endothelium also plays an important role in blood clotting (hemostasis). However, it is also responsible for the development of pathological conditions. Numerous active ingredients or active ingredient precursors are contained in the endothelium. These substances act on the fibrinolytic system. The heparin sulfate and thrombomodulin stored in the endothelium are two important substances with anticoagulant potential. The endothelium is separated from the subendothelial loose connective tissue by a thin basement membrane . This contains elastic fibers , fibroblasts and individual smooth muscle fibers (myointimal cells).
pathology
A tear in the tunica intima , with consecutive flushing through the bloodstream, is a dissection . Intimal hyperplasia can occur after injuries to the tunica intima .
Additional pictures
With hematoxylin-eosin stained specimen of an arterial wall with calcified atherosclerotic plaque
Web links
Individual evidence
- ↑ Hartmut Glossmann : Compendium: Preparatory supplements to the course "From Symptom to Diagnosis to Therapy". Medical University of Innsbruck, 2004.
- ↑ B. Bockholdt: Morphological and histomorphometric examinations of the aortic wall in a comparison group and in deaths from spontaneous (non-traumatic and non-arteriosclerotic) aortic rupture, taking into account forensically relevant issues. Habilitation thesis FU Berlin, 2004.
- ↑ R. Meyer: Blood and Lymph Vessels. In: W. Remmele (Ed.): Pathology. Volume 1, Springer, 1999, pp. 277-341.
- ↑ K. Alexander (Ed.): Vascular diseases. Urban & Schwarzenberg, Munich / Vienna / Baltimore 1993.
- ↑ F. Regainer, W. Schwerdtfeger: histology. Deutscher Ärzteverlag, Cologne 1990, pp. 317-340.
literature
- W. Doerr (Ed.): Organ pathology. Volume I, Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart 1974.