Fushimi Castle
| Fushimi Castle | ||
|---|---|---|
|
Castle tower replica |
||
| Creation time : | 1597 | |
| Castle type : | Hirayamajiro (hill castle) | |
| Conservation status: | received slightly | |
| Place: | Kyoto | |
| Geographical location | 34 ° 56 '15.1 " N , 135 ° 46' 52.3" E | |
|
|
||
The Fushimi Castle ( Japanese 伏見城 , Fushimi-jō ) is located in the district of Fushimi of Kyoto in Kyoto Prefecture . Toyotomi Hideyoshi built the castle as a residence in the Sengoku period .
history
In 1592, Toyotomi Hideyoshi had the castle built on the Shigetsu-no-oka ( 指 月 の 丘 ) hill as a residence. When this castle was destroyed by an earthquake in 1596, Hideyoshi moved the castle to the nearby hill called Kowata-yama ( 木 幡 山 ). In 1597 the five-story castle tower was completed there. In 1598 Hideyoshi died in the castle.
In the skirmishes before the Battle of Sekigahara , the castle was badly damaged in attacks. After the battle, Tokugawa Ieyasu had the castle restored. In 1619 the castle fell under the shogunate's resolution "Only one castle per province" ( 一 国 一条 冷 , ikkoku ichijō-rei ) and was then demolished by 1625. The “Chinese style” ( 唐門 , karamon ) gate of Nishi Hongan-ji is said to come from this castle.
The attachment
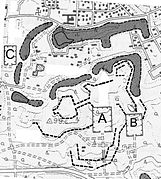
As with many hilltop castles, the innermost area, the Hommaru ( 本 丸 ), is made up of other irregularly shaped areas, the Ni-no-maru ( 二 ノ 丸 ), San-no-maru ( 三 ノ 丸 ) and Yon-no-maru ( 四 ノ 丸) ) surround. In addition, the castle was protected by numerous other defenses:
- A: Harube-shomaru ( 治 部 小丸 ),
- B: Go-Hanabatake-Sansō ( 御 花 畠 山 壮 ),
- C: Tokuzen-maru ( 徳 善 丸 ),
- D: Matsu-no-maru ( 松 の 丸 ),
- E: Nagoya-maru ( 名 護 屋 丸 ),
- F: Ōkura-maru ( 大 倉 丸 ),
- G: Danjō-maru (弾 正 丸),
- H: Sanri-maru ( 山里 丸 ) and
- I: Taki-no-yashiki (瀧 の 屋 敷).
In the south of the hill there was a jetty, J: Go-funa-iri ( 御 舟 入 ). In the south there was also the T1: main gate ( 大 手 門 , ōtemon ). Another important gate, T2: ( 東 大 手 門 , Higashi-ōtemon ), was in the east.
As described above, the castle was completely demolished in the 1620s so it is not very well documented. Remains of the northern trench ( 北 堀 , Kitabori ) in Fushimikitabori Park have been preserved. Excavations are only possible to a limited extent, as the graves of Meiji-Tennō and his wife Shōken are on the southern slope . In addition, the grave of Kammu Tennō from the 8th century is located near the castle grounds .
In 1963, part of the concrete castle was rebuilt on the site of Hanabatake-Sansō. The large castle tower was based on Himeji Castle and the small castle tower on Hikone Castle .
Only after the castle was demolished and the area planted with peach trees was the name Momoyama ( 桃山 , "peach mountain "), after which an entire artistic epoch, the Azuchi-Momoyama period , was later named.
photos
Remarks
- ↑ Shigetsu-no-oka is now called Fushimi-yama, Kowatayana is now called Taichōrō ( 泰 長老 ).
literature
- Yamamoto, Jirō: Kyoto-fu no rekishi sampo (chu). Yamakawa Shuppan, 1998. ISBN 978-4-634-29560-5 .
- Nishigaya, Yasuhiro (Ed.): Fushimi-jo. In: Nihon meijo zukan, Rikogaku-sha, 1993. ISBN 4-8445-3017-8 .