COSO
The COSO ( Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission ) is a voluntary private sector organization in the United States that aims to help improve the quality of financial reporting through ethical conduct, effective internal controls and good corporate governance.
COSO was founded in 1985 as a platform for the National Commission on Fraudulent Financial Reporting ( Treadway Commission ) and is supported by the five most important US organizations for control in finance and accounting: Institute of Internal Auditors (IIA), American Institute of Certified Public Accountants (AICPA), Financial Executives International (FEI), Institute of Management Accountants (IMA) and American Accounting Association (AAA).
The COSO model (1992/94) (COSO I)
In 1992, COSO published a standard for internal controls, the COSO model, which is now recognized by the SEC . This control model is used to document, analyze and design the internal control system (ICS), it is divided into three target categories:
- operational risks
- Financial reporting
- Compliance
The COSO ICS model has gained particular recognition through the US regulations, according to which listed companies must review and report on their accounting-related ICS annually and, if they exceed a certain size, have the system audited by the auditor ( Sarbanes-Oxley Act ).
The components of the internal control system according to the COSO model are:
- Control environment
- Risk assessment
- Control activities
- information and communication
- monitoring
The COSO ERM framework (2004) (COSO II)
In 2004, COSO released a further development of its original model, the COSO ERM - Enterprise Risk Management Framework . This should enable companies to develop or improve their own risk management system.
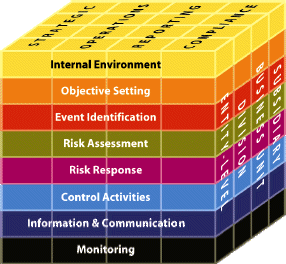
The COSO cube illustrates the three dimensions of the model.
- Components of company-wide risk management
- Internal environment
- Objective setting process
- Event Identification
- Risk Assessment
- Risk Response
- Control activities
- Information and Communication
- Monitoring
- Target categories
- Strategic goals (Strategic)
- Operational goals (Operations)
- Reporting objectives (reporting)
- Compliance goals (compliance)
- Organizational units
- Entire company (entity level)
- Division (division)
- Business unit
- Subsidiary
In 2017 a modernized and expanded version of the COSO ERM framework was published.
The COSO Guide to Internal Control of Financial Reporting in Smaller Public Companies (2006)
The guide, published in July 2006, supplements the COSO framework for internal control from 1994 in order to facilitate its application, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises.
The guide describes 20 basic principles and a process that is made up of the components of the COSO control model.
- Control environment
- Integrity and Ethical Values
- Corporate management
- Management philosophy and style
- organization structure
- Financial reporting ability
- Decision-making authority and responsibility
- Staffing
- Risk assessment
- Financial reporting objectives
- Financial Reporting Risks
- Risk of fraudulent acts
- Control activities
- Integration with risk management
- Selection and implementation of control activities
- Rules and procedures
- Information technology
- information and communication
- Information for financial reporting
- Information about internal controls
- Internal communication
- External communication
- monitoring
- Ongoing and targeted assessments
- Reporting weaknesses
Other control models
CoCo was published in 1995 by the CICA as a more management-oriented, general control model.
COBIT is a control model for IT management that was first published in 1995 and incorporates the basic ideas of the COSO control concepts.
See also
- Corporate governance
- Directive 2006/43 / EC (Auditing Directive)
- ICoFR - Internal control over financial reporting
- Control model
literature
- Christian Brünger: Successful risk management with COSO ERM. Recommendations for the design and implementation in practice . Berlin 2009, ISBN 978-3-503-11439-9 .
- Julia C. Helbeck: Internal Control System in Practice. An implementation guide for managing operational risks in business processes . Saarbrücken 2008, ISBN 978-3-8364-6881-7 (a practical example for implementing the COSO model).
Web links
- The Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission - COSO
- Canadian Institute of Chartered Accountants - CICA
- CobiT - ISACA
Individual evidence
- ^ Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission (COSO) (ed.): Internal Control - Integrated Framework . AICPA, Jersey NY 1992.
- ↑ Christian Brünger: Successful risk management with COSO ERM . Erich Schmidt Verlag Berlin, 2009. ISBN 978-3-503-11439-9 .
- ↑ COSO: Enterprise Risk Management Integrating with Strategy and Performance. Retrieved September 5, 2018 .
- ↑ COSO: Internal Monitoring of Financial Reporting - Guide for Smaller Public Companies. Volume I: Summary. ( Memento from March 4, 2016 in the Internet Archive ) PDF file (376 kB). June 2006.