Chinese dwarf bilch
| Chinese dwarf bilch | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|

Chinese dwarf bilch ( Typhlomys cinereus ) |
||||||||||||
| Systematics | ||||||||||||
|
||||||||||||
| Scientific name | ||||||||||||
| Typhlomys cinereus | ||||||||||||
| Milne-Edwards , 1877 |
The Chinese dwarf bilch ( Typhlomys cinereus ) is a rodent from the family Stachelbilche (Platacanthomyidae). It occurs in southeast Asia .
features
This rodent reaches a head-trunk length of 7 to 10 cm, a tail length of 9 to 14 cm and a weight of about 18 grams. Although the species is one of the spiny lobsters, it has no spines in its fur and is more like a common house mouse . The short, dense fur is soft. The Chinese dwarf bilch is dark gray on the top and slightly lighter on the underside with the exception of the white front paws. At the tip of the tail there is a tassel of hair, which is often white. Near the root, the tail is sparsely hairy and partly covered with scales . The narrow hind legs and the small eyes are striking.
Distribution and habitat
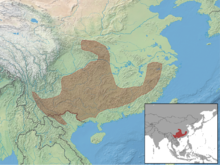
The distribution area extends over the southeastern People's Republic of China and the northernmost regions of Vietnam . The species may also be found in northern Laos . The Chinese dwarf bilch inhabit mountainous landscapes up to 2,000 meters above sea level. Most of the forests in these regions are characterized by small trees and a dense undergrowth of bamboo . Sometimes the dwarf bilch is found in different types of forests.
Way of life
These rodents live in underground nests, but not as predominantly as blind mole rats . Otherwise almost nothing is known about their behavior.
status
The total population is decreasing, but this is not yet a serious risk, and so the species is listed as Least Concern by the IUCN . The population in North Vietnam was given the status of a subspecies by some zoologists, Typhlomys cinereus chapensis, and was declared an independent species ( Typhlomys chapensis (Osgood 1932)) in mid-2014 because it differs greatly from the main population. This is considered to be threatened with extinction.
literature
- Ronald M. Nowak: Walker's Mammals of the World . Johns Hopkins University Press, 1999 ISBN 0801857899
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b Nowak, RM (1999) p. 1432 Google books
- ↑ a b c Typhlomys cinereus in the endangered Red List species the IUCN 2011. Posted by: Lunde, D. & Smith, AT, 2008. Accessed September 22, 2012 found.
- ↑ Alexei V Abramov, Alexander E Balakirev and Viatcheslav V Rozhnov. 2014. An enigmatic Pygmy Dormouse: Molecular and Morphological Evidence for the Species Taxonomic Status of Typhlomys chapensis (Rodentia: Platacanthomyidae). Zoological Studies. 53:34. DOI: 10.1186 / s40555-014-0034-2