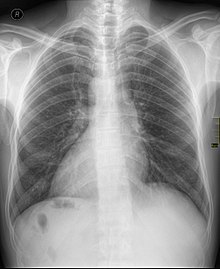
Dextrocardia
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| Q24.0 | Dextrocardia |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |

Computed tomogram of a dextrocardia (seen from below, left in the picture)
With the term Dextrokardie ( Rechtsherzigkeit ) derived from gr. Dexios = "right" and cardiac = "heart" is in medicine refers to a phenomenon in which the heart permanently or temporarily in the predominantly right instead of the left thoracic cavity is .
Dextrocardia can occur congenitally as part of a so-called situs inversus (totalis), in which all organs in the chest or in the whole body are mirror-inverted. Also dextrocardia may be caused by a heart rotation about as a result of a lung - or pleural disease .
Some people with Patau syndrome (trisomy 13) have dextrocardia, while the other organs are laid out as usual.
Web links
Individual evidence
- ^ Klaus Holldack, Klaus Gahl: Auscultation and percussion. Inspection and palpation. Thieme, Stuttgart 1955; 10th, revised edition, ibid 1986, ISBN 3-13-352410-0 , p. 191.