Wireworm
The larvae of beetles from the family of click beetles (Elateridae) are called wireworms , of which the rapid beetle is one of the representatives.

|
|

|
|
| Wireworm - close up of the head | |

|
|
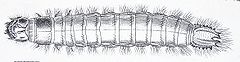
| Image 1: Larva of Agriotes lineatus | |
|
|
| Image 2: Larva of Agrypnus murinus | |

|

|
| Image 3: top | Photo 4: underside |
| of the head of the larva of Agrypnus murinus , all illustrations after Reitter , Fauna Germanica | |
They are often round and, due to the armor with chitin, stiff and relatively hard, which is where the name comes from. They have three pairs of legs, strong jaws and pointy eyes on the top of the head (picture 3). Due to the shape of the last abdominal segment (anal segment) that is characteristic of each species (picture 1, picture 2), they are relatively easy to determine. The wireworms of the species living in the tree mole are carnivorous . They live predatory on other larvae and maggots and can also eat each other. The species living in the ground are herbivores (phytophag).
The larvae of some species of this beetle family are considered pests in the forest , in agriculture and in horticulture . They feed underground on the roots of young plants and seedlings. In tree nurseries and plant gardens in particular, the larvae can cause severe damage. In forest pine seedlings , the damage can be seen, for example, when the needles wither . They even eat freshly laid seeds such as acorns .
In agriculture, they can cause great damage to underground parts of grain, maize, root crops and legumes. The natural development site for the click beetles is grassland, which is why there are a particularly large number of larvae there. If crops are planted on plowed grassland, particularly severe damage can be expected there in the following years.
The feeding damage to the adult beetles, however, is insignificant. The beetles mainly eat young deciduous and softwood shoots. Feeding marks can be found during the months of May, June and July.
Text source
- Adolf Horion: Beetle science for nature lovers . Vittorio Klostermann, Frankfurt am Main 1949
Individual evidence
- ↑ Review of ten years of attempts to control wireworm. Bavarian State Institute for Agriculture. On LfL.Bayern.de, accessed on October 5, 2019.