Patch test
The patch test or patch test is a provocation test ( allergy test ) that is used to determine whether a contact allergy is present. The patch test is currently the only means of detecting late allergies (in which there is a longer period between exposure and reaction).
method
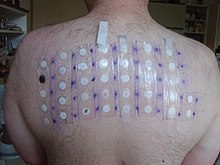
The allergens to be tested (e.g. nickel , dyes) are fixed on the skin with a plaster for about 48 hours. A cream with a chemical solution containing the allergens in question is applied to these patches. The patch is then removed and the first reading is taken. Their results are compared with a second reading taken after a further 24 hours in order to better distinguish allergic reactions from toxic ones. Possibly. you even have to wait another 24 hours.
During the time of the test, the skin should not be exposed to water to prevent the allergens from being washed out . If the patient is taking drugs that block or reduce the immune response, false negative test results may occur. It is also important to ensure that the contact points are not already stressed (irritated, eczema, etc.), as otherwise false positive results may be caused (so-called " angry back ").