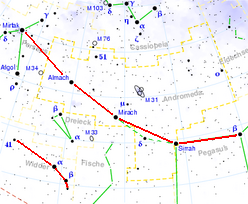
Five star row
A five- star row is a bright, about 60 ° long row of stars that runs from the constellation Perseus over the three main stars of Andromeda to Pegasus . Due to its location close to the pole, it can be seen almost all year round. The 5 stars are all of the second size , so they belong to the brightest 50 stars in the northern sky.
In the evening , the five-star row is best seen in autumn , when it is almost at its zenith . In winter and spring it extends from near the zenith to almost the west and northwest horizons, and in the summer sky in the second half of the night from the east towards the zenith. In the middle of the star row (3 ° north) you can find the Andromeda Nebula , which appears freely-eyed as a small cloud.
The name was coined around 1920 by Oswald Thomas , the founder of the Transylvanian and Austrian Astro Association and the Vienna Astronomical Office . The term soon established itself in amateur astronomy through his specialist and popular books and hundreds of star evenings he held on Sommerhaidenweg .
The stars in the five-star sequence are from east to west:
Individual evidence
- ↑ Oswald Thomas, Heaven and Universe. Neff-Verlag, 4th edition (1951)
- ↑ Gerhard Fasching: Constellations and their myths. , Springer-Verlag (1994), ISBN 978-3-7091-3378-1 , page 32