Geographic Names Information System
Geographic Names Information System ( GNIS ) is a database that contains the names and location information of nearly two million geographic objects in the United States and the dependent territories. GNIS was set up by the United States Geological Survey in collaboration with the United States Board on Geographic Names (BGN) to promote the standardization of the naming of geographical objects.
Content of the database
The database contains the names of geographic objects and references to topographic maps , including information on geographic location and bibliographic references. Books and historical maps that confirm the existence of a geographical object are recorded in the database, including deviating historical or alternative, unofficial names.
At the end of 2014, GNIS contained 2,726,567 names for 2,268,566 geographic objects in the United States.
The GNIS database uses 63 broad, historically grown categories, feature classes (formerly feature types ), such as "stream" for flowing water, "populated places" (ppl) for cities and inhabited places, "lake" for lakes, etc.
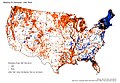
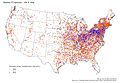
- Distribution maps for names in GNIS
Geographical objects with parts of their name "Coulee" (orange) or " Bayou " (blue)
Other authorities for naming geographical locations
- The Bureau of the Census defines census-designated places , which can consist of several locations named in the GNIS.
- The US Postal Service Publication 28 sets standards for addressing mail. The Postal Service defines two-digit letter codes that designate the state , as well as fixed abbreviations for streets, such as Boulevard (BLVD) and Street (ST) or subordinate distinguishing features such as Suite (STE).
- The name of the US Postal Service post offices was previously used to determine place names.
Name changes
Proposals for changing the names of geographical objects can be sent to the GNIS, whereby evidence must be provided that the proposal is justified; the submission of lists of supporters is required.
Publications on the topic
- US Department of the Interior, US Geological Survey, National Mapping Division, Digital Gazeteer: Users Manual, (Reston, Virginia: US Geological Survey, 1994).
- Heat Moon, William Least, Blue Highways: A Journey Into America , (Boston: Little Brown and Company, 1982).
- Jouris, David, All Over The Map , (Berkeley, California: Ten Speed Press, 1994.).
- Report: "Countries, Dependencies, Areas Of Special Sovereignty, And Their Principal Administrative Divisions," Federal Information Processing Standards, FIPS 10-4.
- Report: Principles, Policies, and Procedures: Domestic Geographic Names, US Board of Geographic Names, 1997.
- US Postal Service Publication November 28 , 2000.
See also
- GEOnet Names Server , a similar database for areas outside of the United States
- Geographical Names Board of Canada , a similar body for Canada
Web links
- Geographic Names Information System . Website, English.
Individual evidence
- ↑ Annual Report To the Secretary of the Interior, Fiscal Year 2014 . United States Board on Geographic Names (BGN). Retrieved October 29, 2015.
- ↑ Domestic Names - Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) BGN
- ↑ Feature Class Definitions USGS