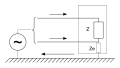
Push-pull signal
A push-pull signal is called a signal that is sent to all inputs of a module that are relevant to the function, e.g. B. at the inputs of an operational amplifier , applied simultaneously with opposite phase. Push-pull voltage signals are called push-pull voltages. In the case of currents, one speaks of push-pull current. Symmetrical signal transmissions are an example of push-pull signals.
Real signals are usually a superposition of common-mode and differential- mode signals .
example
The following figures show a common mode signal, a push-pull signal and the superposition of the two signals for real power distribution.
literature
- Joachim Franz: EMC. Fail-safe construction of electronic circuits, Teubner Verlag, Stuttgart Leipzig Wiesbaden 2002, ISBN 3-519-00397-X .
See also
Web links
- High frequency technology (accessed on July 12, 2018)
- Differential amplifier (accessed July 12, 2018)