Joint task to improve the regional economic structure
The federal states are responsible for improving the regional economic structure . In accordance with Article 91a of the Basic Law for the Federal Republic of Germany , the federal government participates in this task if it is significant for the whole and if federal assistance is required to improve living conditions. To improve the regional economic structure, the federal and state governments jointly undertake the following measures:
- Investment promotion of the commercial economy in the construction, expansion, conversion or fundamental rationalization of commercial enterprises,
- investment support for business-related infrastructure, insofar as it is directly necessary for the development of the regional economy,
- non-investment and other measures to strengthen the competitiveness of companies, to flank structural problems with regional policy and to support regional activities insofar as they are directly necessary for the development of the regional economy,
- Evaluation of the measures and accompanying regional political research.
history
The first measures to promote the economy - cabinet resolution of July 3, 1951: demarcation of the redevelopment areas - contained a DM 100 million funding program, which the Bundestag approved on July 2, 1953. The so-called emergency areas and the so-called border area were designated as the redevelopment area . Between 1954 and 1959 these areas were combined in the new “regional funding program of the federal government”. If economic development was limited to low-interest loans until the aforementioned laws were passed, investment grants or grants were now granted for the individual investments . This had tax advantages for the entrepreneur , at the same time with this type of promotion - with the same high use of the available financial resources - a much more targeted promotion was achieved.
Funding target
The aim of the joint task is to promote investments in the individual regions in order to generate additional income within the region and to bring structurally weak regions to the general economic structure.
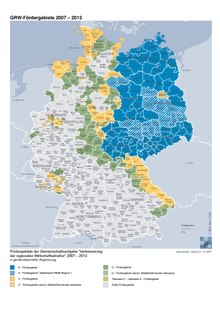
Eligible area
Today's GA has its origins in the “central local program” of 1959. In this, economic promotion was carried out for the first time as a spatial and selective promotion according to priorities. The actual breakthrough of the GRW took place in 1968, when the BMWi developed proposals for intensifying and coordinating regional structural policy, which resulted in the Investment Allowance Act and found its legal basis in the law on the joint task “Improvement of the regional economic structure”, or GRW for short.
The planning committee that was set up initially developed a “master plan” every year in which the individual support areas and support measures were defined. Today's master plans usually run for three to four years.
Funding instruments
Funding can consist of grants, loans and guarantees.
Head
The funding is still available today at different levels, divided according to the importance of the so-called focus locations (whereby a focus location can also include a region). The individual funding rates changed. The current (as of November 2007) funding rates are as a percentage of the investment for small / medium-sized / other operating facilities:
- Main locations with the code number A: 50% / 40% / 30%
- Main locations with the code number C: 35% / 25% / 15%
- Focus areas with the code number D: 20% / 10% / max. 200,000 euros in three years
In addition, as part of the new version of the funding guidelines effective January 1, 2007, acquisition costs of intangible assets can be subsidized up to 50 percent of the eligible investment costs (previously up to 25 percent).
Zone border funding
All areas along the former border with the GDR and Czechoslovakia were referred to as the “ border area ” . These areas were funded within a community-specific strip with a width of 40 kilometers along the former border to the GDR with the highest funding level (A). This was intended to prevent the population from migrating to the industrialized areas of West Germany.
Overall, it was possible to receive one-off subsidies of around 55 percent of the total investment within the zone border subsidy and also to receive permanent subsidies of up to 25 percent.
European Union
The GRW has been harmonized with the funding programs of the European Union (EU). The design and implementation of the funding programs remain with the member states, but these must remain within the framework of the regulations set by the Commission and in individual cases can lead to significantly increased funding.
swell
- Hans Hermann Eberstein (Hrsg.): Handbook of regional economic development. Loose-leaf collection. Schmidt, Cologne from 1971. Main volume : ISBN 3-504-40000-5 .
Web links
- GRW law
- Federal Ministry of Economics and Technology: Joint task "Improvement of the regional economic structure" (GRW)
- Strengthening the economy in the regions, article: "Federal and state joint task to improve regional economic structures" , BMI
- Coordination framework for the joint task “Improvement of the regional economic structure” from September 17, 2018 , BMI