Gilman-Moore reaction
The Gilman-Moore reaction is a name reaction in organic chemistry. It was first described in 1957 by the American chemists Henry Gilman (1893-1986) and Leonard O. Moore. It is used for the synthesis of phenoxazine .
To the reaction
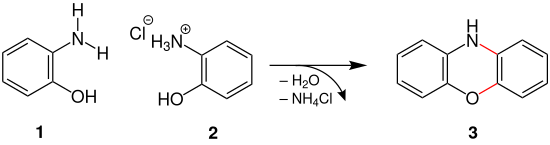
This reaction makes it possible to synthesize phenoxazine 3 at up to 295 ° C. starting from 2-aminophenol 1 and its hydrochloride 2 with elimination of water and ammonium chloride . When the phenoxazine heterocycle closes, two bonds are newly formed, these are marked in red in the figure :
Individual evidence
- ^ Henry Gilman, Leonard O. Moore: The Preparation of Some 10-Substituted Phenoxazines . In: Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1957, Vol. 79, No. 13, pp. 3485-3487, https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01570a048 .
- ↑ a b Eberhard Breitmaier, Günther Jung: Organic Chemistry: Basics, Compound Classes, Reactions, Concepts, Molecular Structure, Natural Products, Synthesis Planning, Sustainability Vol. 7. Georg Thieme Verlag, Stuttgart, 2012, p. 697, ISBN 978-3-13- 541507-9 .
- ^ Entry on Gilman-Moore reaction. In: Römpp Online . Georg Thieme Verlag, accessed on April 14, 2020.