Hard fat
| Glycerides (examples) * Lauric acid residue ( blue ) * Myristic acid residue ( red ) |
|---|
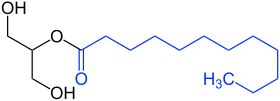 Monoglyceride |
 Diglyceride |
 Triglyceride |
Hard fat (Adeps solidus) is a mixture of mono-, di- and triglycerides , which is obtained from palm kernel oil and coconut oil . It is preferably used in pharmaceutical production as an excipient in the manufacture of suppositories .
Composition and properties
Hard fat consists mainly of saturated C 12 -C 18 fatty acids that are esterified with glycerol , with lauric acid dominating. Due to the presence of mono-, di- and triglycerides, the hard fat shows emulsifying properties . Hard fat is a white, waxy and brittle mass that is practically insoluble in water and only sparingly soluble in ethanol .
Depending on the manufacturer and type, hard fats differ in their melting temperature , hydroxyl number and saponification number . The European Pharmacopoeia, however, requires a melting temperature of 30 to 45 ° C, a hydroxyl number less than 50 and a saponification number between 210 and 260. The respective exact value must be specified by the manufacturer.
Uses and benefits
Hard fat is preferred for making suppositories because of some advantages over cocoa butter . Hard fat serves as a carrier in which the active ingredient is dissolved or dispersed.
Hard fat has a longer shelf life due to the lack of triglycerides of unsaturated fatty acids. In addition, the melting temperature can be influenced by adjusting the fatty acids, thereby compensating for effects of the active substance that lower or increase the melting point. As it cools, hard fat shows a significant contraction in volume, which makes it easier to remove it from the mold.
Individual evidence
- ^ Bracher, Franz; Heisig, Peter; Langguth, Peter; Mutschler, Ernst; Rücker, Gerhard; Scriba, Gerhard KE; Stahl-Biskup, Elisabeth; Troschütz, Reinhard; Seitz, Gunther; Schirmeister, Tanja (Ed.): Pharmacopoeia Commentary . 2016th edition. Scientific publishing company Stuttgart.
- ↑ a b European Pharmacopoeia 9th Edition | EDQM - European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines. In: www.edqm.eu. Retrieved January 3, 2017 .
