Lifting weir
A siphon weir is a special type of weir which, thanks to its structure, can drain off larger amounts of water per time than conventional weirs with the same cross-section. The principle of pressure drainage is used here. Siphon weirs are used where water has to be removed quickly if necessary, e.g. B. in relief structures for dams .
Structure and principle of operation
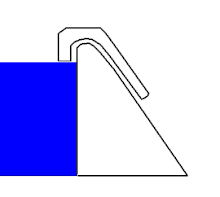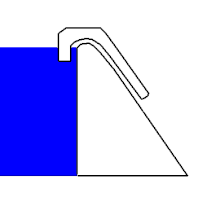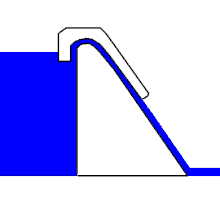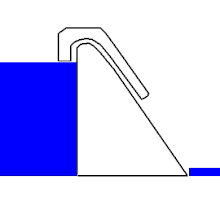
The siphon weir is one of the fixed weirs and consists of a normal weir crown, over which a lid is placed according to the shape of the crown. This creates the so-called siphon hose , which is only open to the upper and lower water. The starting nose is also an important part of a lift weir .
If the water level in the upstream water rises , a gravity drain is created in the siphon hose as in conventional weirs, i. H. inside the siphon hose the water flows with a free surface and is subject to the laws of channel hydraulics . At the lower end of the siphon hose, the water is directed over the starting nose.
When the outflow becomes large enough, the water jet directed via the starting nose closes the lower end of the siphon hose airtight. The flowing water gradually pulls the air out of the siphon hose, similar to a water jet pump . This will completely deflate the hose until the water flows under pressure drainage conditions, i.e. H. the flow no longer has a free surface and is subject to the laws of pipe hydraulics . The siphon weir now sucks in the upper water in the form of a suction siphon and enables a large drainage and a lowering of the upper water below the height of the weir crown. This is e.g. As desired in spillways to in a reservoir to lower the water level to a safe level.
The process continues until air enters the siphon hose. This happens either when the water level of the upper water has dropped far enough and the weir sucks in air or when air is manually let into the hose through valves . The discharge of pressure and thus also the suction of the upper water is stopped abruptly.
commitment
Since large flows can be reached quickly with a siphon weir, this design was particularly popular in the past as a component of flood relief systems for dams . A relatively large relief system from several, lifter battery called lifter weirs was z. B. installed at the Roßhaupten storage facility in Bavaria.
Due to the comparatively complicated structure, the limited controllability and because they cannot be overloaded like a conventional weir, siphon weirs are only an addition to other relief structures.
literature
- Theodor Strobl, Franz Zunic: Hydraulic engineering. Current principles, new developments . Springer, Berlin a. a. 2006, ISBN 3-540-22300-2 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ a b c d e Peter Rißler: Talsperrenpraxis . Oldenbourg Industrieverlag, 1998, ISBN 978-3-486-26428-9 , p. 156 f .
- ↑ K. Zilch, CJ Diederichs, R. Katzenbach: Handbook for civil engineers: Technology, organization and economy - specialist knowledge in one hand . Springer Verlag, 2002, ISBN 978-3-540-65760-6 , pp. 5-113 .