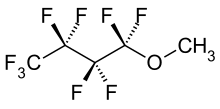
Hydrofluoroether
| This item has been on the quality assurance side of the editorial chemistry entered. This is done in order to bring the quality of the articles on the subject of chemistry in terms of form and content to the level desired in Wikipedia. We are grateful for your help , please take part in the discussion ( new entry ) or revise the article accordingly. |
Hydrofluoroethers (HFE) are among the fluorinated organic compounds. They were originally developed to replace ozone-depleting chemicals such as CFC , HFC , HCFC and PFC . They are colorless and almost odorless, tasteless, have a low viscosity and have a boiling point above room temperature.
Because of their high molecular weight , they only have a very short atmospheric lifespan , which is less than two weeks. Although it is a greenhouse gas , the EPA does not regulate its use as it has a short life span in the atmosphere and zero ozone depletion potential compared to alternative chemicals . The 3M company sells these liquids under the trade name Novec. Commercially available are for example Methylnonafluor- n -butyl ether , Methylnonafluor- iso -butyl ether , Ethylnonafluor- n -butyl ether and Ethylnonafluor- iso -butyl ether or mixtures thereof.
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ W. Tsai: Environmental risk assessment of hydrofluoroethers (HFEs). In: Journal of Hazardous Materials . 119, 2005, p. 69, doi : 10.1016 / j.jhazmat.2004.12.018 .
- ↑ a b Barbara Kanegsberg, Edward Kanegsberg: Handbook for Critical Cleaning . CRC Press, 2000, ISBN 978-1-4200-3982-5 , pp. 88 ( limited preview in Google Book search).
- ↑ Cleaning with hydrofluoroether (HFE). All-Electronics.de, September 24, 2007, accessed on July 24, 2019 .