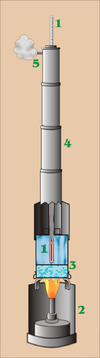
Hypsometer
A hypsometer (from agr. Ὕψος hýpsos, "altitude" and μέτρον métron, "measure") is a device for barometric altitude measurement .
The hypsometer can be designed as an aneroid (as described for the first time by Lucien Vidie in 1844 ) or act like a hypsothermometer .
Technical design of the hypsometer also called boiling barometer : pure water is heated to boiling with a spirit burner, a constant temperature is set in the steam room. This is measured with a high-resolution thermometer (usually a maximum thermometer that records the highest temperature reached). The air pressure can be calculated from the measured value, and from this the local altitude using the barometric altitude formula. The accuracy of the method is limited by the resolution of the thermometer. It is also influenced by the weather-related pressure fluctuations in the atmosphere.