Intercarrier process
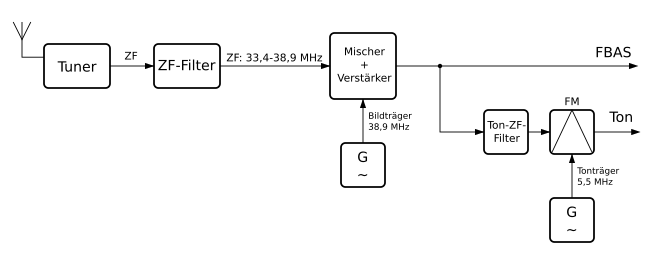
The intercarrier process , intermediate carrier process or differential carrier process is used in television technology for reception with single-channel sound. The frequencies 33.4 MHz to 38.9 MHz are filtered out of the frequency mix at the tuner output with a broadband intermediate frequency filter .
The IF picture carrier, the IF sound carrier and the IF color carrier are amplified in the common IF amplifier. In the shared demodulator, mixing the signal with the carrier frequency 38.9 MHz (= picture carrier) and the IF sound carrier (33.4 MHz) creates the sound carrier with 5.5 MHz.
At the output of the demodulator, the BAS signal and the chrominance signal voltage of 4.43 MHz are present as the difference between the IF picture carrier and the IF color carrier. The sound carrier is filtered out, amplified and demodulated in an FM demodulator.
The advantage of the intercarrier method is that an almost constant sound carrier IF and color carrier IF arise even if the transmitter setting in the tuner is inaccurate, since the frequencies of the video carrier, the sound carrier and the color carrier only fluctuate at most 3 kHz against each other. Another advantage is that the audio carrier IF voltage (33.4 MHz) is also amplified in the picture IF amplifier, which means that amplifier stages can be saved. However, since IC are mostly used today, the additional installation of amplifier stages causes only low costs.
The disadvantage of the intercarrier method, however, is that mutual interference can occur between the image signal and the audio signal, since both signals are amplified in the image IF amplifier. If the audio signals are too large, picture disturbances in the form of a moire occur. Image signals can cause sound interference. A strong limitation of the audio IF voltage in the audio IF part is therefore necessary. Intercarrier humming can occur particularly when text lines are faded into the television picture and if the picture amplitude is too large. Such sound disturbances are particularly noticeable in stereo transmission.
- See also: parallel tone method , quasi parallel tone method