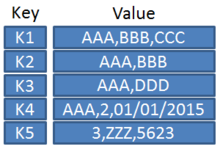
Key-value database
A key value database (also known as a key value database or key value store ) is used for electronic data management in computer systems . It is based on the key-valued data model to associative arrays to store.
The associated software is the key-value database management system . Key-value databases are assigned to the NoSQL databases. This implies that they are not only operated with the SQL commands from relational databases , but also enable and require additional functions due to their properties. Values ( Value ) in key-value databases via a key ( Key clearly identified). The values can consist of tuples , relations or documents (see document-oriented database ). In particular, it is possible that the structure of two keys is different, which allows more flexibility and avoids the storage of placeholders for non-existent values.
providers
The most widespread key-value memory in April 2020 is the open source software Redis . Other systems include:
- Amazon Dynamo
- Berkeley DB
- DBM
- Google BigTable
- Lightning Memory-Mapped Database
- memcached
- Project Voldemort
- Riak
literature
- Adam Fowler: NoSQL For Dummies . John Wiley & Sons, Chichester 2015, ISBN 978-1-118-90574-6 , pp. 95-138 .
- Joe Celko: Joe Celko's Complete Guide to NoSQL . What Every SQL Professional Needs to Know about Non-Relational Databases . Morgan Kaufmann, Burlington 2013, ISBN 978-0-12-407192-6 , pp. 81-88 .
Individual evidence
- ↑ DB Engines: Ranking of key value stores. Retrieved April 14, 2020 .