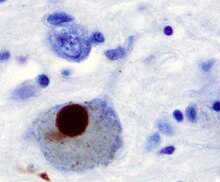
Lewy corpuscles
Lewy bodies (English: Lewy bodies ) are characteristic structures in the brain tissue of patients who are alive to Parkinson's disease or dementia of the Lewy body type , are detectable have suffered. These are round cytoplasmic inclusion bodies of nerve cells . They usually have a dense, eosinophilic core and a pale halo. They are made up of α-synuclein , ubiquitin , neurofilament and other protein deposits.
Lewy bodies were first associated with Parkinson's disease in 1912 by the neurologist Friedrich H. Lewy (1885–1950). Their ultrastructure was first described by Duffy and Tennyson in 1965. While Lewy bodies are found in nerve cells of the substantia nigra in Parkinson's disease, in Lewy body dementia they occur in the brain stem and in the cerebral cortex , among other things .
Original work
- E. Forster, FH Lewy: Paralysis agitans. In: M. Lewandowsky (Ed.): Pathological Anatomy. Manual of Neurology. Springer Verlag, Berlin 1912, pp. 920-933.
- PO Duffy, VM Tennyson: Phase and electron microscopic observations of Lewy bodies and melanin granules in the substantia nigra and locus coeruleus in Parkinson's disease. In: J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 24, 1965, pp. 398-414.