Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes
The Logical Observation Identifiers Names and Codes ( LOINC ) is a database with general names and identifiers for the designation of examination and test results from laboratory and clinic. The aim is to facilitate the electronic data exchange when transmitting medical examination results and diagnostic data. For the exchange of structured documents ( CDA ) and messages, the use of LOINC by HL7 and DICOM is recommended. The terminology is constantly being expanded and regularly published in the form of a database; the maintenance and documentation of the LOINC database is the responsibility of the Regenstrief Institute (Indianapolis, USA). In Germany, the introduction of LOINC is funded by DIMDI , which also takes on the exchange of information with the responsible national and international institutes, project groups and industry.
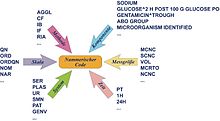
The following fields are used to specify a LOINC expression:
- Component (analyte) - e.g. B. Potassium, hemoglobin, hepatitis C antigen
- Measured property (measurand) - e.g. B. substance concentration, enzyme activity (catalysis rate)
- Time information - either an examination at a certain point in time or an examination within a certain period of time - e.g. B. 24 hour urine
- Type of sample (system) - e.g. B. urine, whole blood, plasma, liquor.
- Type of scaling - e.g. B. whether the measurement was quantitative (dimensional accuracy), ordinal (with graduated alternatives), nominal (e.g. Escherichia coli , Staphylococcus aureus ) or as a text representation (e.g. the result after dictation in X-ray examinations).
- If necessary, indicate the method by which the result was obtained or other observations were made.
In addition to the data fields for this six-part designation for each LOINC, the database contains abbreviations, reference words, synonyms and comments for all investigations. Additional informative information is contained in other data fields for many codes (e.g. typical units of measurement , standard ranges for samples, CAS numbers ).
See also
literature
- Clement McDonald, Gunther Schadow, Jeffrey Suico, Kai U. Heitmann: Do you speak LOINC? (PDF; 609 kB) . HL7-Mitteilungen Issue 8, year 2000, ISSN 1616-8909 .
- M. Dugas, S. Thun, T. Frankewitsch, KU Heitmann: LOINC codes for hospital information systems documents: a case study. In: Journal of the American Medical Informatics Association: JAMIA. Volume 16, number 3, 2009 May-Jun, pp. 400-403, doi : 10.1197 / jamia.M2882 , PMID 19261942 , PMC 2732230 (free full text).