Object Exchange Model
The Object Exchange Model ( OEM ) has established itself as the de facto standard for storing semi-structured data . "It was originally developed for the Tsimmis (The Stanford-IBM Manager of Multiple Information Sources) project."
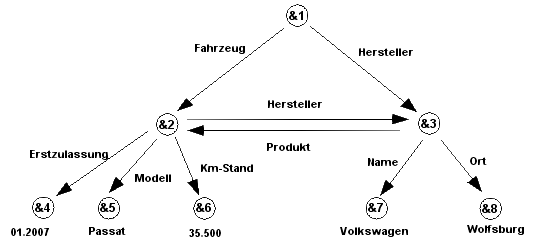
The OEM model is based on the conception of a directed graph . “A (directed) graph is a pair G = (V, E), where V is a finite set of nodes and E V V is a relation on V, the set of edges.” However, leaves Va also exist within an OEM model from which no edges can lead away.
The nodes of an OEM graph represent the actual objects that have a unique ID . Within an OEM model, a distinction is made between complex objects Vc and atomic objects Va. The attributes of complex objects are described only by the edges that turn on complex objects or atomic objects reference . In addition, the graph contains one or more roots r1 to rk, from which all objects must be accessible. The atomic objects represent the leaves of the graph, i.e. that is, there can only be one edge leading to them, but none leading away. The atomic objects contain the values of the complex objects m to which they are assigned of the type integer , string , image or the like. 3
"Formally, semi-structured data can be defined as G = (V, E, r1, ..., rk, v) with:
V = Vc Va: the set of nodes, where Vc is the set of complex objects and Va is the set of atomic objects;
E Vc A V is the set of edges, where A is the set of all attributes;
ri is the amount of roots;
v: Va D a mapping that assigns values from D, the set of all atomic values, to atomic objects. ”4
|
| Example of an OEM graph |
Basically, the Cartesian product Vc V defines all possible edges of the graph. This means that all complex objects can be referenced with all objects. However, atomic objects cannot have a reference to complex objects.
Greiner has expanded this Cartesian product by the factor A (the set of all attributes): Vc A V. This expresses that the subset of edges can be assigned to any cheap attribute. Thus, the elements of the subset of the edges E are also assigned an attribute; the set of attributes is not explicitly included in the basic set G of the graph.
The same applies to the set of all possible values D, which are assigned to the atomic objects with the mapping Va D.
In principle, the abbreviations of the graph also belong to the set of complex objects. The roots must meet the condition that all nodes can be referenced from them. To show an example of a graph with two roots, the root in Figure 1 can be omitted:

|
| Example of an OEM graph with two roots |
Thus & 2 and & 3 are roots.
1) 2) 3) 4)
literature
- Ulrike Greiner: Semi-structured data . 1999 ( online [accessed August 10, 2017]).



