Partial tide
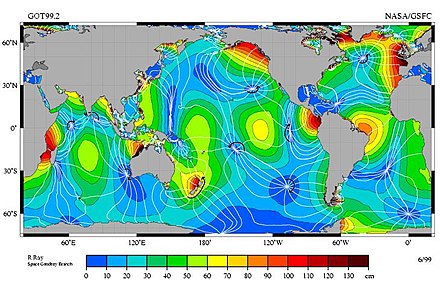
Amplitude of the M 2 partial tides in the world's oceans. In the amphidromic points the amplitude is zero.
As partial tides in are tide customer the individual harmonics called that form the recurring basis of Tidegeschehens in their superposition. The height of ebb and flow that can be measured at a coastal gauge is ultimately additionally z. B. increased or decreased by wind congestion . A partial tide is described by the amplitude and frequency of its oscillation.
The four most important partial tides that make up the largest part of the entire tidal process are the half-day lunar and solar tides and the one-day lunar and declination tides . The eight most important partial tides with their abbreviations are listed in the following, non-exhaustive table.
| designation | Surname |
|---|---|
| M 2 | half-day main moon tide |
| S 2 | half-day main tide |
| K 1 | one day main declination tide |
| O 1 | one-day main moon tide |
| N 2 | large elliptical first order tide to M 2 |
| K 2 | half day main declination tide |
| μ 2 | large variation tide to M 2 |
| P 1 | one day main solar tide |
literature
- Andreas Malcherek: Tides and waves: The hydromechanics of the coastal waters . Springer-Verlag, 2009, ISBN 978-3-8348-9764-0 .
Individual evidence
- ^ Analysis of the partial tides. Federal Institute for Hydraulic Engineering, accessed on August 8, 2014 .