Backflow level
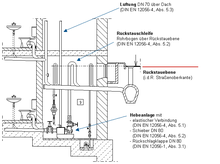
The backflow level ( RSTE or RSE for short ) marks the highest possible level of wastewater at a certain point in a sewer system .
In DIN EN 12056-1: 2000 (gravity drainage systems within buildings) it is defined as "the highest level up to which the water in a drainage system can rise".
Backwater can occur during heavy rainfall and floods , so rainwater and mixed sewers are particularly at risk. However, line blockages or the flushing of lines can also lead to backflows, so that backflows can also occur in waste water channels in separation systems. According to the principle of communicating pipes, there is a risk that the water from the sewer will penetrate into the building through sanitary objects below the backflow level, causing extensive damage. Connected sanitary objects and all other drainage points below the backflow level must be protected against backflow by a lifting system , backflow protection or other closures.
The upper edge of the street at the junction of the property drainage canal is considered to be the decisive backflow level, unless otherwise specified by the relevant sewer works.