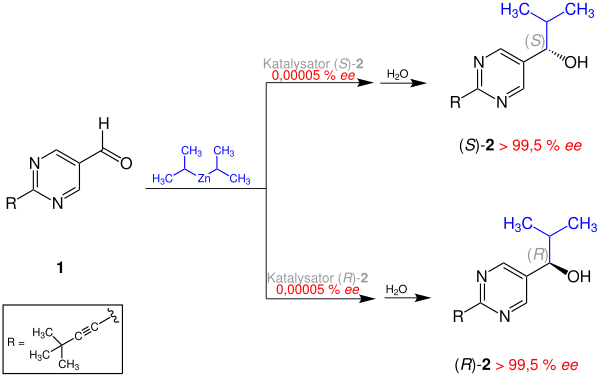
Soai reaction
The Soai reaction is an alkylation reaction of pyrimidine-5-carbaldehyde with diisopropylzinc . The resulting product - a pyrimidyl alcohol - acts as an autocatalyst: Using small amounts of the same catalyst with a low enantiomeric excess ( ee ) results in a product with a high ee value. Starting with a pyrimidyl alcohol, with an extremely low ee of approx. 0.00005%, a product with> 99.5% ee is obtained in three autocatalysis cycles , an increase by a factor of approx. 630,000.
The Japanese chemist Kensō Soai (* 1950) discovered this reaction in 1995.
See also
Individual evidence
- ↑ Chirality and Life: A Short Introduction to the Early Phases of Chemical Evolution , pp. 16-17.
- ↑ Takanori Shibata, Hiroshi Morioka, Tadakatsu Hayase, Kaori Choji, Kenso Soai: Highly Enantioselective Catalytic Asymmetric Automultiplication of Chiral Pyrimidyl Alcohol . In: Journal of the American Chemical Society . 118, 1996, p. 471. doi : 10.1021 / ja953066g .
Further literature
- DG Blackmond: Asymmetric Catalysis Special Feature Part II: Asymmetric autocatalysis and its implications for the origin of homochirality . In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences . 101, 2004, p. 5732. bibcode : 2004PNAS..101.5732B . doi : 10.1073 / pnas.0308363101 .
- Prof. Kenso Soai
- JR Islas: Mirror-symmetry breaking in the Soai reaction: A kinetic understanding . In: Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences . 102, 2005, p. 13743. bibcode : 2005PNAS..10213743I . doi : 10.1073 / pnas.0503171102 .
- KáRoly Micskei, Gyula Rábai, Emese Gál, Luciano Caglioti, Gyula Pályi: Oscillatory Symmetry Breaking in the Soai Reaction . In: Journal of Physical Chemistry B . 112, No. 30, 2008, p. 9196. doi : 10.1021 / jp803334b . PMID 18593153 .
- THE CONCEPT OF RACEMATES AND THE SOAI-REACTION . Retrieved December 27, 2013.
- Joachim Podlech, Timo Gehring: New Aspects of Soai's Asymmetric Autocatalysis . In: Angewandte Chemie International Edition . 44, 2005, p. 5776. doi : 10.1002 / anie.200501742 .
- Joachim Podlech, Timo Gehring: Advances in asymmetric autocatalysis according to Soai . In: Angewandte Chemie . 117, 2005, p. 5922. doi : 10.1002 / ange.200501742 .