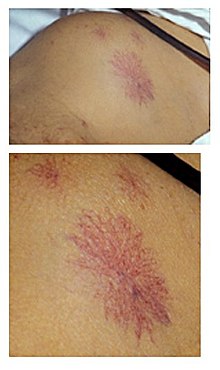
Nevus araneus
| Classification according to ICD-10 | |
|---|---|
| I78.1 | Nevus, non-neoplastic |
| ICD-10 online (WHO version 2019) | |
The nevus araneus or nevus stellatus , also known as spider nevus , star nevus , or vascular spider or Eppinger's asterisk (English spider nevus , plural spider naevi), is a frequent and benign arterial neoplasm of the skin . Starting from a central, raised vascular nodule the size of a pinhead, thin runners (vascular fissures) pull outwards like spiders or stars. If you press a spider nevus with a glass spatula, the runners disappear, but the red central vessel does not.
Spider nevi are usually found in the upper half of the body (face, neck, hands, upper trunk area ). They are the most common form of telangiectasia and are often idiopathic (with no apparent cause) in children.
In addition, they can often occur eruptively during pregnancy , hormonal contraception, liver diseases such as liver cirrhosis , CREST syndrome , chronic UV damage and steroid abuse .
Spider nevi are an aesthetic problem for many patients. A laser treatment usually leads in these cases to cosmetically satisfactory results. However, a cause should be sought beforehand (see above).
Individual evidence
- ↑ M. Sand, D. Sand, C. Thrandorf, V. Paech, P. Altmeyer, FG Bechara: Cutaneous lesions of the nose. In: Head & face medicine. Volume 6, 2010, p. 7, ISSN 1746-160X . doi: 10.1186 / 1746-160X-6-7 . PMID 20525327 . PMC 290354 (free full text). (Review).
- ^ A b S. M. Finn, M. Rowland, F. Lawlor, W. Kinsella, L. Chan, O. Byrne, O. O'Mahony, B. Bourke: The significance of cutaneous spider naevi in children. In: Arch Dis Child . 91 (7), Jul 2006, pp. 604-605. Epub 2006 Apr 4. PMID 16595646
- ↑ E. Tan, C. Vinciullo: Pulsed dye laser treatment of spider telangiectasia. In: Australasian Journal of Dermatology . 38 (1), Feb 1997, pp. 22-25. PMID 9046648